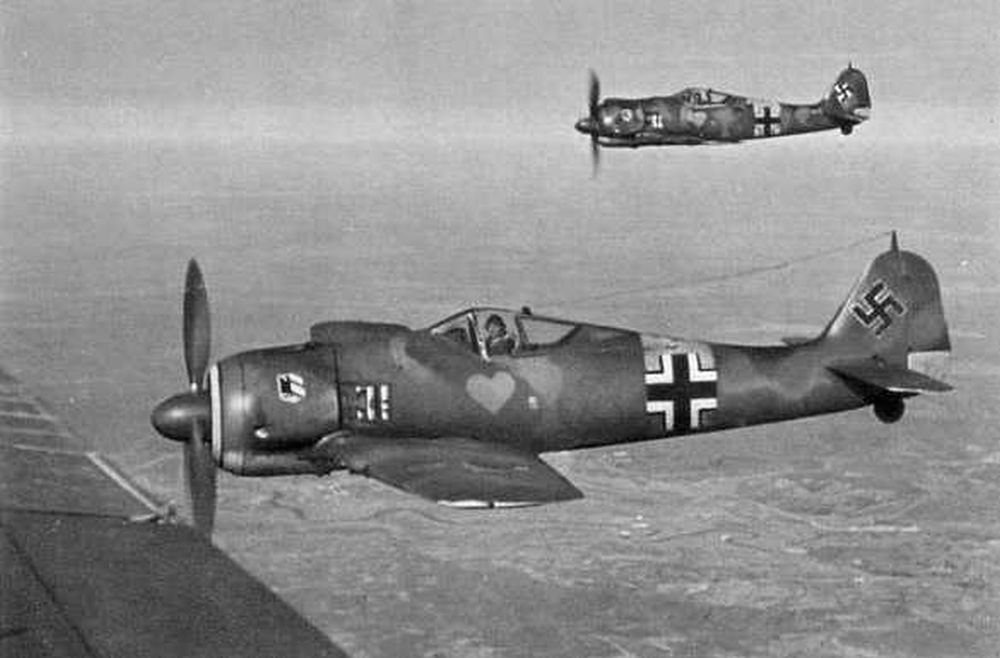
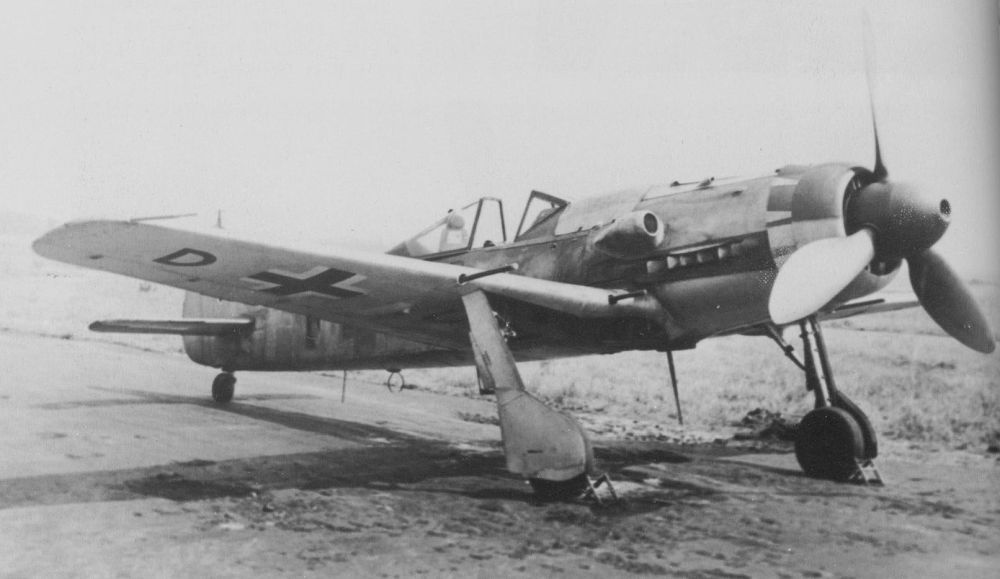
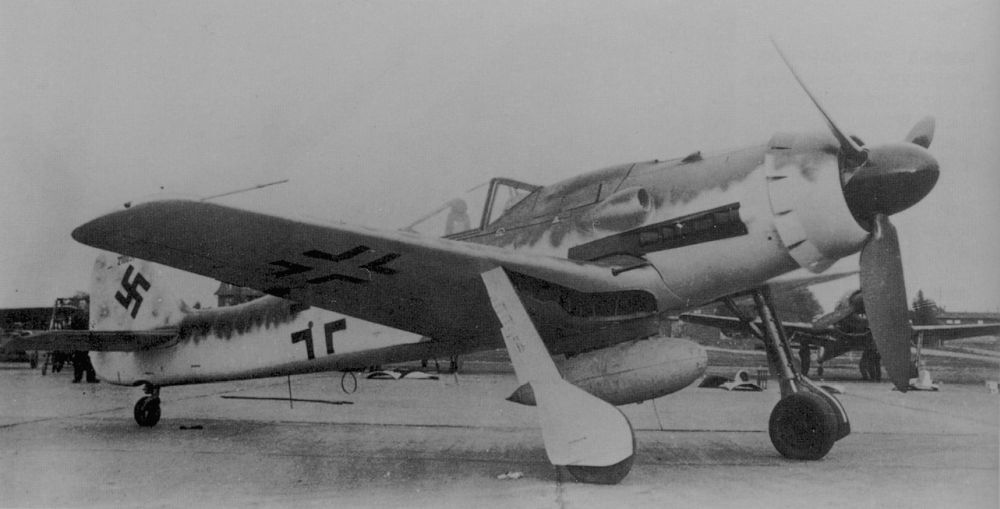
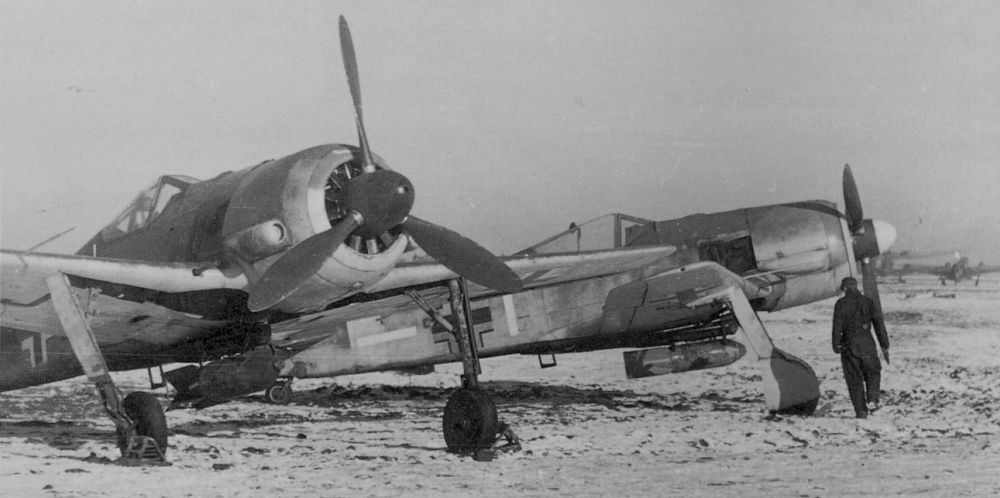
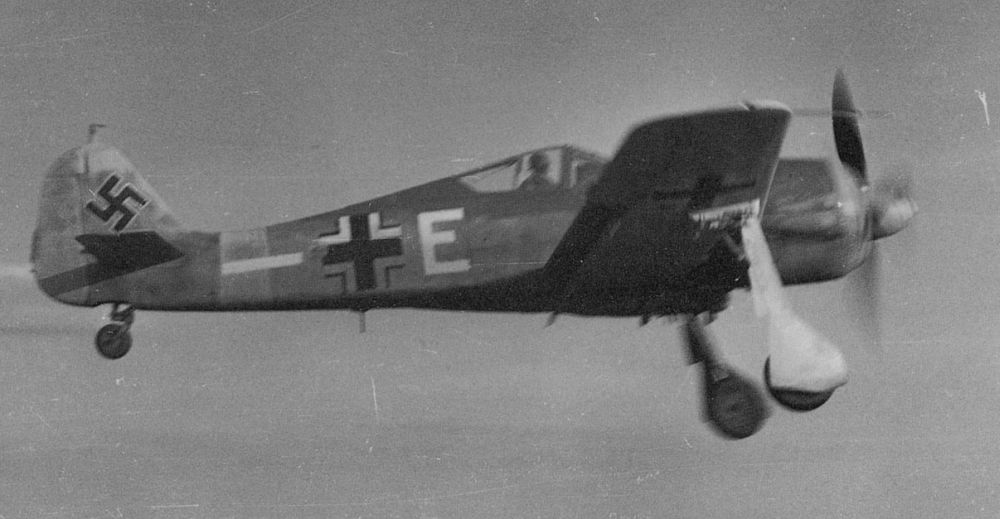
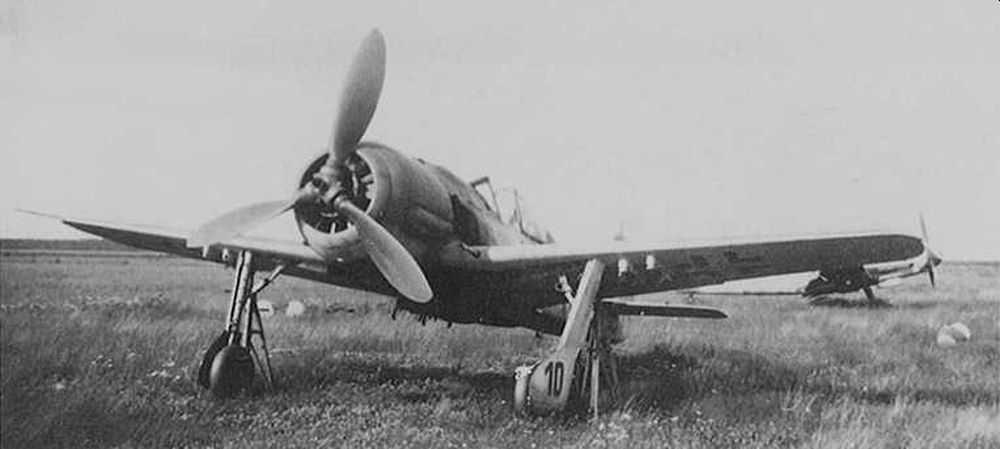
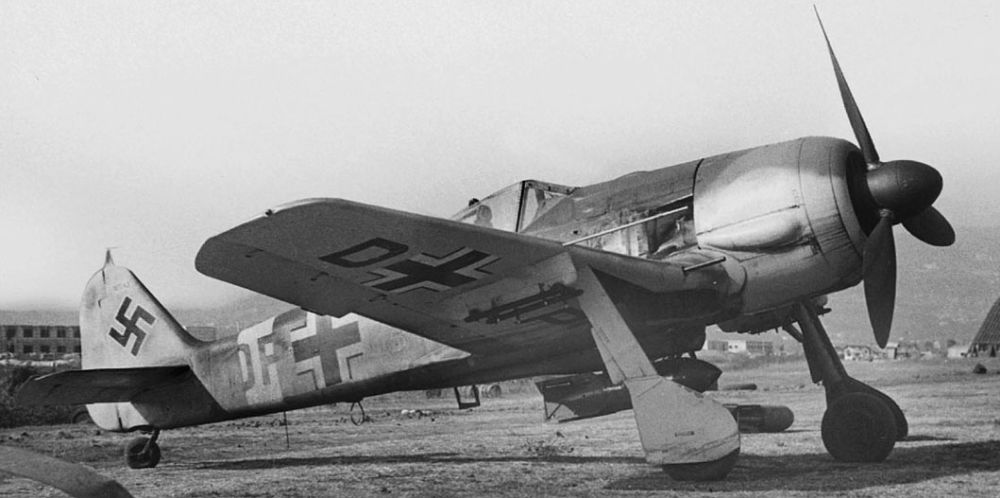
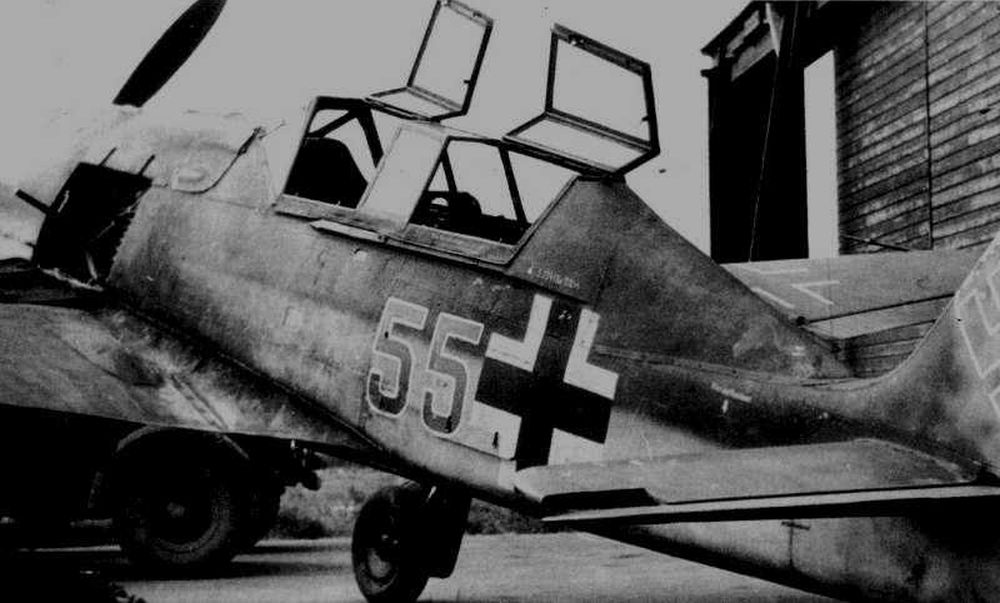
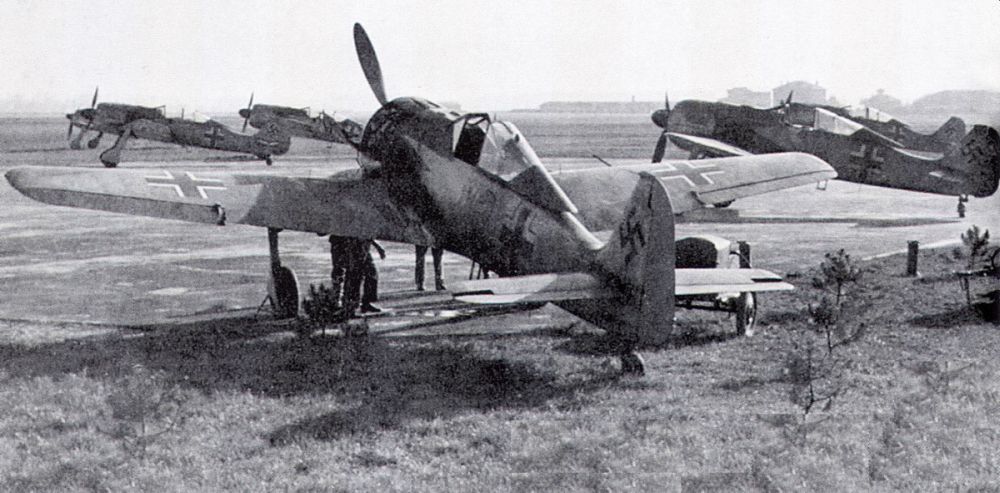
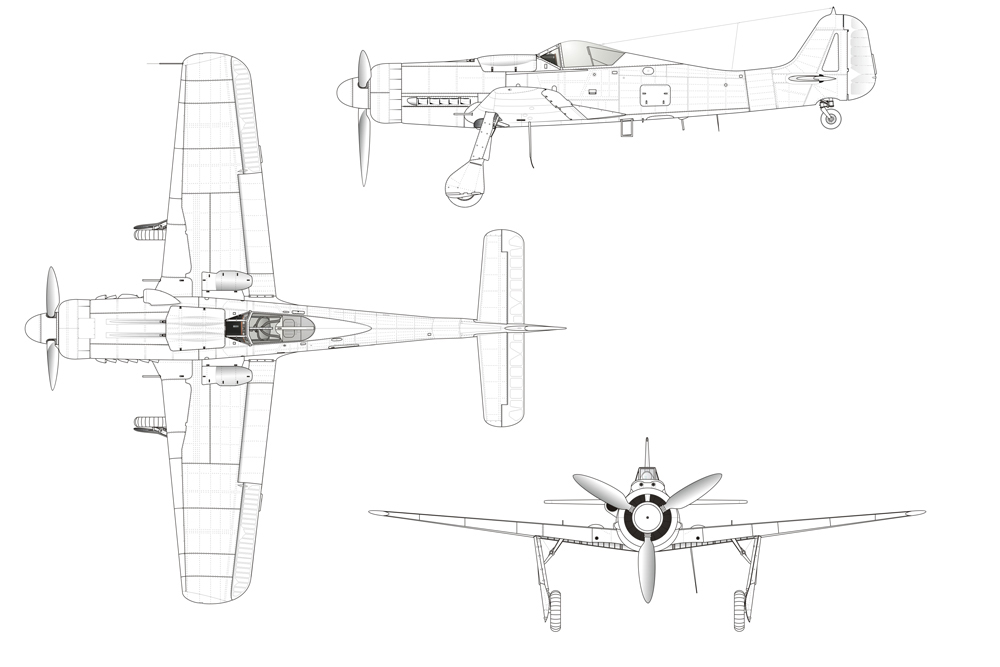
Introduction
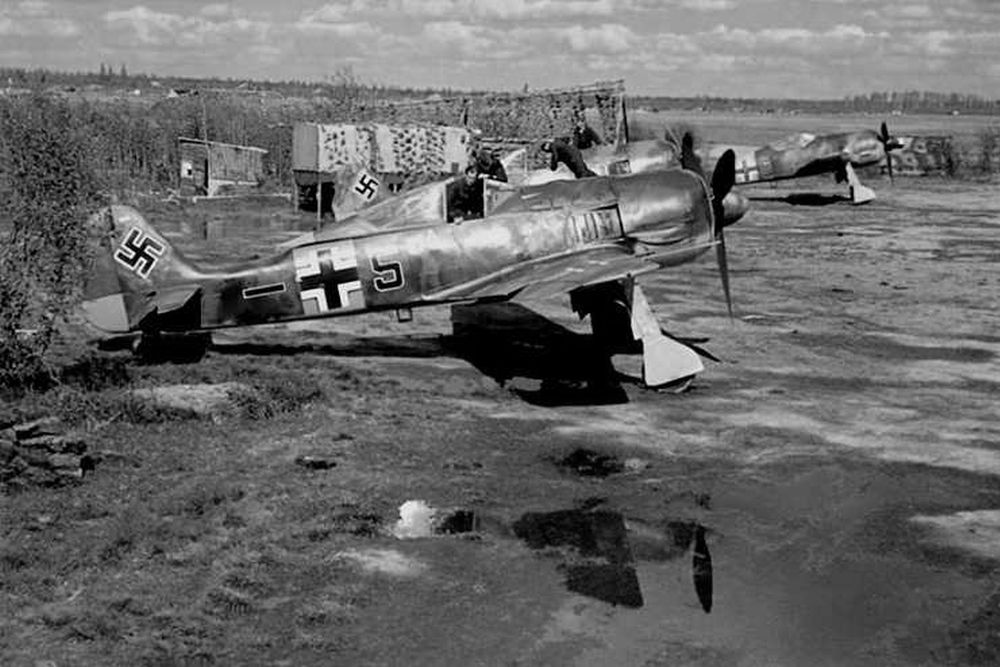
In addition to the Messerschmitt Bf 109, the Focke Wulf Fw 190 belongs to the most important fighter aircraft of the Luftwaffe during World War Two. When the Fw 190 entered service in 1941, it could rightfully claim the title best fighter in the world. It performed far better than the best Allied fighter of the day, the Supermarine Spitfire Mk V. More than a year later, a new generation of Spitfires, the Mk IX, would match the Fw 190. After that time, this fighter was an even match for the best Allied fighters due to its excellent adaptability.
Definitielijst
- Luftwaffe
- German air force.
Development
This aircraft appeared in the fall of 1937 when the German Reichsluftfahrtministerium (Ministry of Aviation) considered it no longer justified to depend on just one type for the fleet of fighters. Supervised by engineer Kurt Tank, the Focke Wulf works suggested two fighters of the same type, each with a different engine, namely the Daimler-Benz DB601 and the BMW 139. Eventually the latter was selected. One of the main reasons was that production of the Daimler-Benz engine was already rather overburdened as those were the most widely used engines in Germany. In the summer of 1938, the final design was presented. The Fw 190 had become a compact, aggressive looking fighter entirely constructed from metal.
Prior to serial production, at least five prototypes were built. Of almost every subsequent version, a prototype was built again, highly increasing the total number of prototypes. In total, seven basic versions were produced, each version with a large number of subversions. Within these subversions, many divergences were possible. In this way, nearly 20,000 units were produced.
| type | details | prod |
| Fw 190V | prototype | 6 |
| Fw 190A | base version | 13,000 |
| Fw 190B | BMW 801 turbo | 3 |
| Fw 190C | DB 603 engine | 8 |
| Fw 190D | high altitude | <1,800 |
| Fw 190E | not produced | 0 |
| Fw 190F | ground attack | 700 |
| Fw 190G | fighter bomber | ca 1,300 |
| Fw 190S | trainer | 58 |
Prototypes
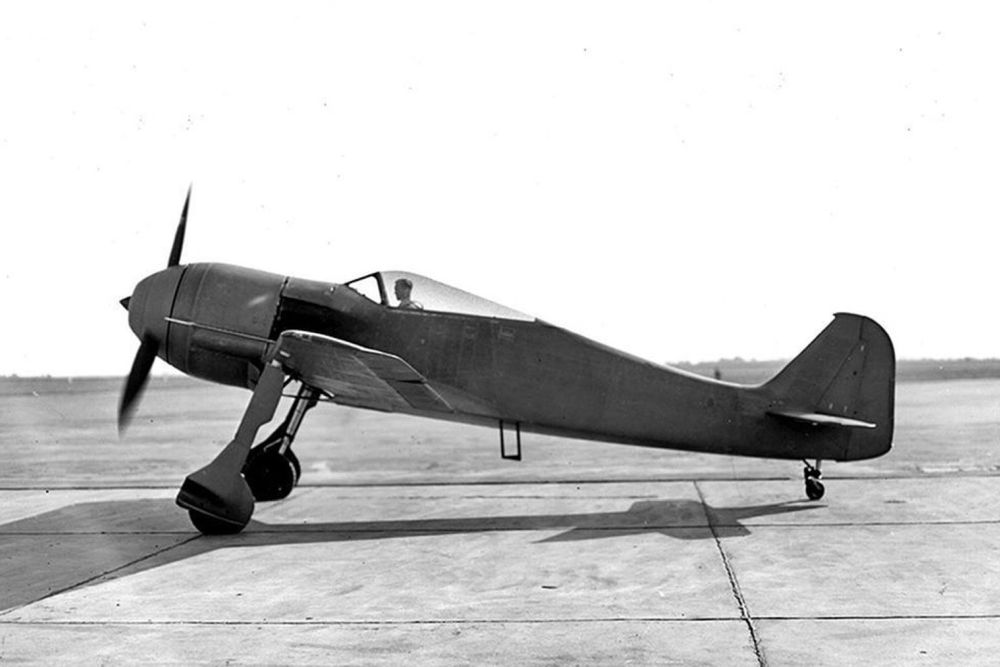
The first prototype, the Fw 190V-1, made its maiden flight in June 1939 and was propelled by a 1,550hp BMW 139 engine. Although the flying characteristics proved to be excellent, problems soon popped up due to the engine overheating. In October, the second prototype , FW 190V-2, appeared with the same engine but armed with two 7.92mm machineguns on the nose and two 13mm MG in the wings, close to the fuselage. Location of these weapons became the standared although calibre varied in the course of time. The problem with the overheating engine hadn't been solved yet though.
In order to solve these problems, a new engine was required and the V-3 and V-4 were scratched. Eventually, the BMW 801C- became the new engine and consequently the design of the aircraft had to be adapted slightly. For testing, two prototypes were built, the Fw 190V-5k (short wing) – wingspan 31ft, wing surface161 sgft and the Fw 190V-5g (larger wing), wingspan 34ft, wing surface 197sqft. The latter was to become the standard wing. Of the Fw 190, no less than 54 prototypes were built. For almost every version of the Fw 190, a prototype has been built prior to production.
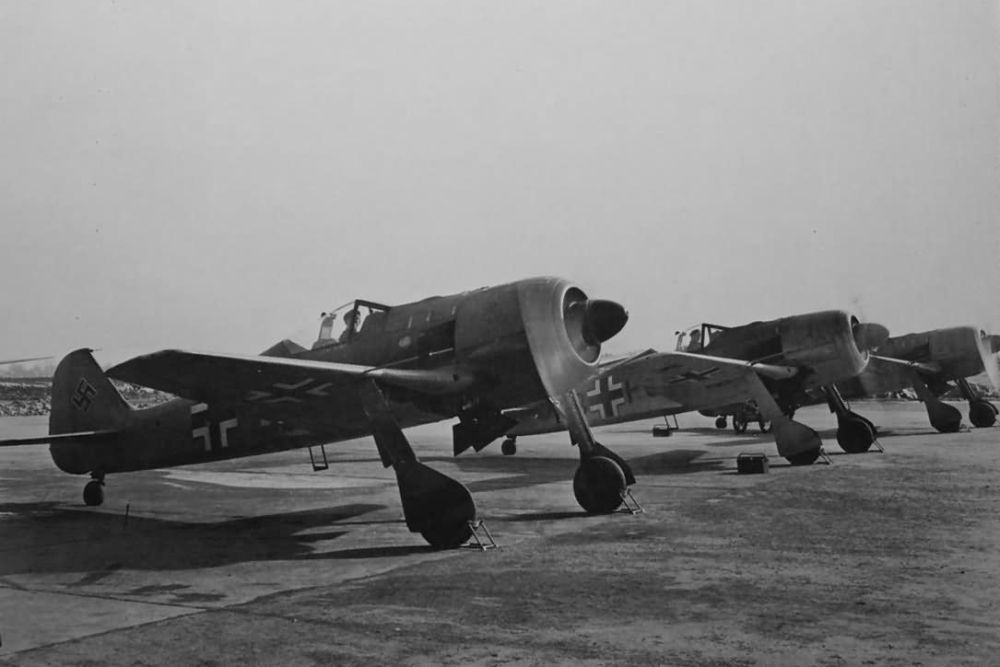
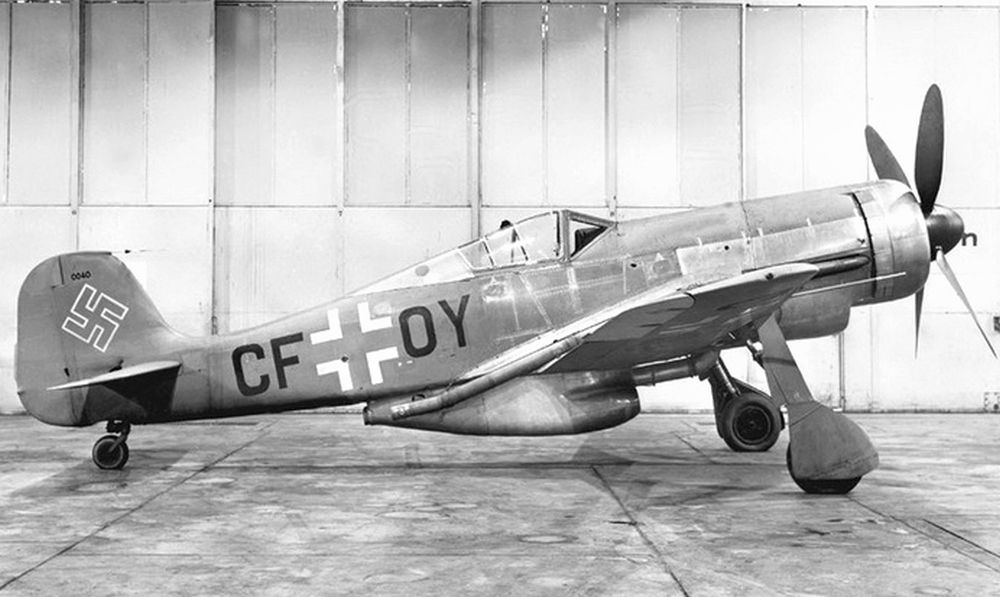
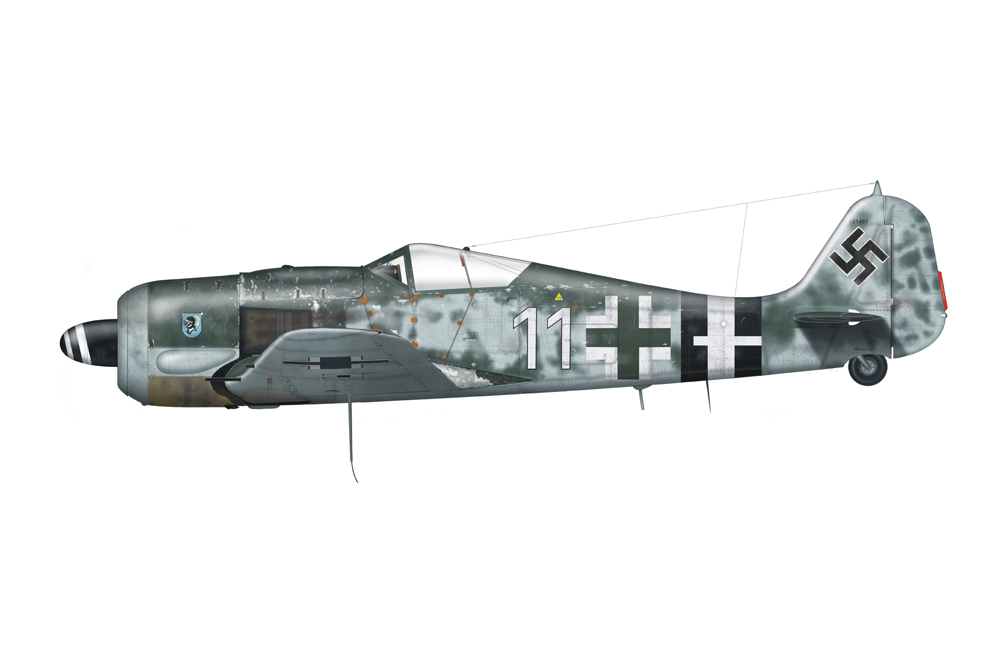
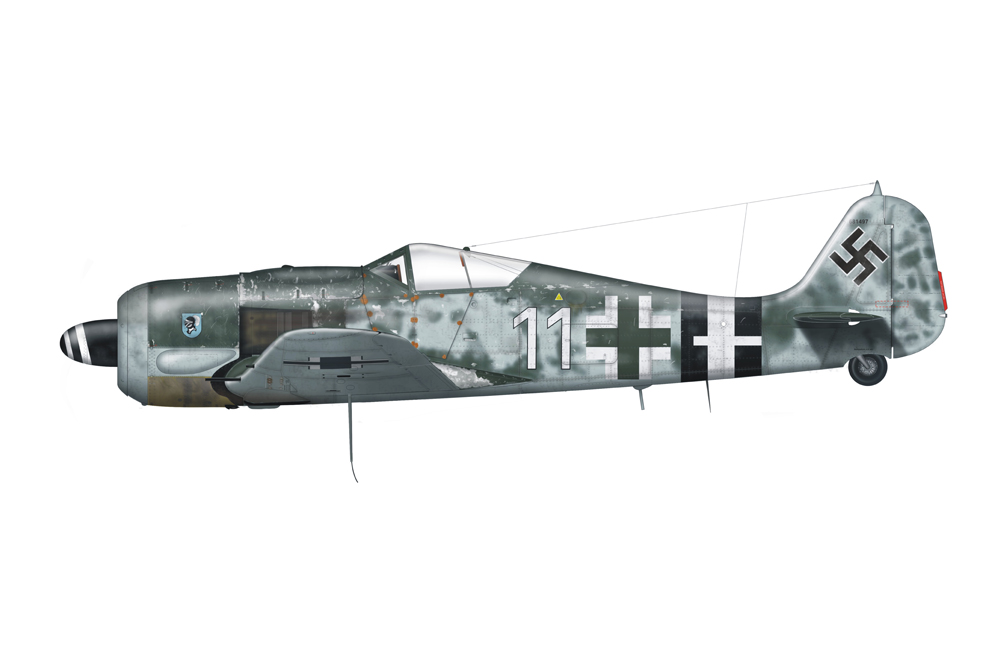
FW 190A
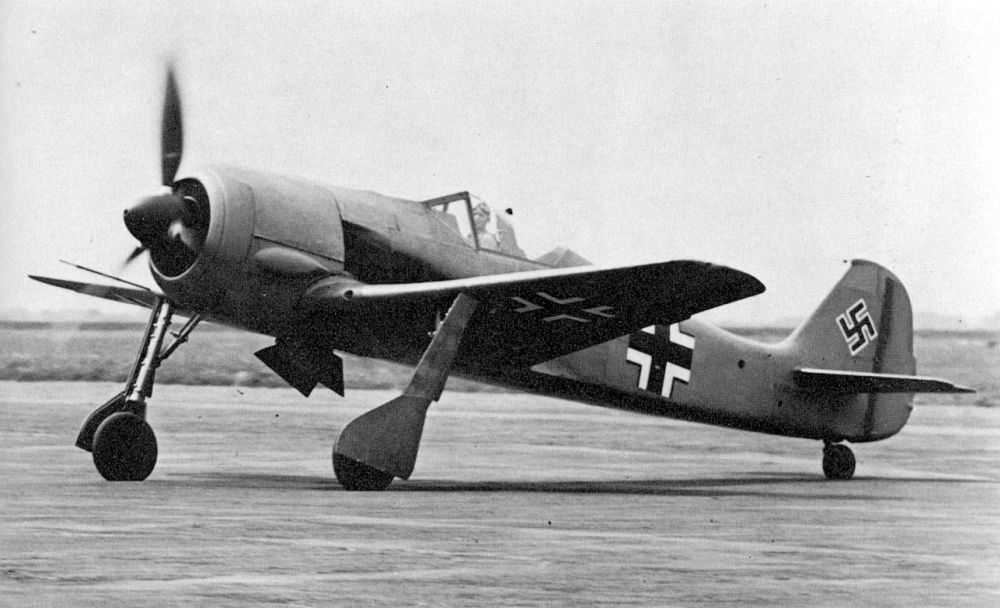
After the tests with the last two prototypes, an order for 40 aircraft of the Fw 190A-0 pre-series with the BMW 801C-1 engine and four 7.92mm machineguns was placed. Eventually, only 28 were completed. The first batch of seven was delivered with the short wing but overall performance of the larger wing was such that the remaining 21 units were constructed with this larger wing.
After the first operational tests had been successfully completed, 120 aircraft of the follow-up series, the Fw 190A-1, were ordered. The A-1, looking like the Fw 190V-5g prototype in every way, was propelled by a BMW 801C-1 engine and armed with four 7.92mm Rheinmetall-Borsig MG 17 machineguns. Two of these were fitted on top of the nose and the two others in the root of the wing, all synchronized to fire through the air screw. The first five aircraft were used for testing and hence designated Fw 190V-7 to V11.
The first operational aircraft were delivered to II Staffel, JG 26 in northern France. This squadron was one of the remaining squadrons at the Western Front as all others had been sent to the Eastern Front. The first aircraft entered service in August 1941. In order to produce all those fighters, apart from Focke Wulf, the works of AGO and Arado were called upon. Eventually, 102 aircraft of the A-1 series were produced.
Soon it became clear that the A-1 series lacked firepower. Meanwhile, tests had been conducted with two 20mm MG FF/MM Ikaria cannon in the wings. Firepower was enhanced although an insufficient amount of ammunition could be carried. Propelled by the newer BMW 801C-2, increasing the weight to a maximum of 7,715lbs, speed increased to 404mph. With this engine and the new armament of two MG 17 machineguns and two MG 151/20 cannon, the Fw 190A-2 was born of which 426 were produced. The first units were again destined for JG 26 which received them in November 1941. In April 1942 all Gruppen of this squadron had switched to this new type.
Towards that time, the factory had developed the Fw 190A-3 which can be considered the first real production model of which no less than 509 units were built. The A-3 was almost identical to the A-2 but was propelled by a 1,700hp BMW 120-D2 engine. In addition, better armor had been added and in case of emergency, the canopy could be jettisoned.
In March 1942, the first aircraft went to northern France, again to JG 26. However, this time JG 1 received its first Fw 190A-3s. This type is also the only type that has been exported. In the years 1942 and 1943, Turkey received no less than 72 aircraft of a slightly adapted version, the Fw 190Aa-3. This was also the version that fathered numerous subversions. Fighter-bomber versions – Fw 190A-3U1, U3 and U7 – were produced that could be armed with a 1,100lbs SC-500 bomb using the Umrüst-Bausatz ETC 501 or conversion kit. In order to save weight, the cannon in the wings were removed. Another subversion was the 3/U4 scout plane that could be equipped with one or two Rb 12.5/7 cameras. This version of the A-3 was also the first Fw 190 deployed over the Soviet Union. Only one U/1 has been produced which was the base of the prototype of the A-5. The A-3 has also been tested with a RZ-65 73mm guided missiles beneath the wing, designated /U2.
In order to use more conversion kits, the Fw 190A-4 was produced in the summer of 1942. This was actually an A-3 with a different radio and a BMW 801D-2 engine, upgraded to 2,100hp, increasing its speed to 416mph. A total of 894 aircraft have been built until well into 1943; the table below shows the various subversions.
Subtypes Fw A-4, ?= production unknown.
- Fw 190A-4/U1: fighter-bomber; two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon, one ETC-501 rack for a 1,100lbs bomb. ?
- Fw 190A-4/U3: fighter-bomber, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon, two 7.92mm MG 17, one ETC-501 rack for a 1,100lbs bomb, 30
- Fw 190A-4/U4: scout plane, one or two Rb 12.5/7 cameras ?
- Fw 190A-4/U8: fighter-bomber, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon, one ETC-501 rack for a 1,100lbs bomb and two ETC-501 racks for two 634 pint drop tanks ?
- Fw 190A-4/Trop: fighter-bomber for North-Africa with dust filters, survival kit and one ETC-501 rack for a 550lbs bomb ?
- Fw 190A-4/R6: two 21cm Wgr. 21 rockets to attack bombers.
In order to fill the need of more conversion kits, the standard Fw 190A-4 frame was adapted by moving a BMW 801D-2 engine 6" forward. The new airplane, now 29ft long, had a better center of gravity and became the Fw 190A-5. The 723 units produced of this version since early 1943 knew many variations. The version most used was the A-5/R6 equipped with two 21cm Wgr. 21 rockets beneath the wings to attack bombers. The table below shows more versions.
Subtypes Fw 190A-5, ?= production unknown.
- Fw 190A-5/U1: fighter-bomber, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon, two ETC-501 racks 1,100lbs bomb each. ?
- Fw 190A-5/U2: night fighter/ fighter-bomber with flame suppressors, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon, one ETC-501 SC-500 1,100lbs bomb, two 79 gallon drop tanks. ?
- Fw 190A-5/U3: two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon, two 7.92mm MG 17, one ETC-501 SC-500 1,100lbs bomb ?
- Fw 190A-5/U4: scout plane, one or two Rb 12.5/7 cameras ?
- Fw 190A-5/U8: fighter-bomber, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon, one ETC-501 rack for a SC-500 1,100lbs bomb and two ETC-501 racks for two 634 pint drop tanks. ?
- Fw 190A-5/U9: bomber killer, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon, two 13mm MG 131 on top of the nose. ?
- Fw 190A-5/U10: fighter, two 7.92mm MG 17, four two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon in the wings. ?
- Fw 190A-5/U11: fighter, two 7.92mm MG 17 on the nose, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon in the wing roots, two 7.92mm MG 17 on the nose, two 30mm MK cannon in nacelles ?
- Fw 190A-5/U12: bomber killer, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon in the wing roots, two 13mm MG 131 on top of the nose, four 20mm MG 151/20 cannon in two external nacelles ?
- Fw 190A-5/U13: long range fighter-bomber, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon in the wing roots, one ETC-501 rack for an SC-500 1,100lbs bomb, two ETC-250 racks for an SC-250 550lbs bomb or 79 gallon drop tanks. ?
- Fw 190A-5/U<14/b>: torpedo bomber, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon in the wing roots, one LTF-5b torpedo. ?
- Fw 190A-5/U15: torpedo bomber, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon, one 2,100 LT-950 torpedo. ?
- Fw 190A-5/U16: ground support fighter, two 7.92mm MG 17 on the nose, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon in the wing roots and two 30mm MK 108 cannon in the center of the wing. ?
- Fw 190A-5/U17: ground support fighter, two 7.92mm MG 17 on the nose, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon in the wing roots and four 110lbs SC-50 bombs in four ETC-50 racks. ?
- Fw 190A-5/Trop: one ETC-501 rack for a SC-250 550lbs bomb, filters and a survival kit for operations in North-Africa. ?
For evaluation and development for her own industry, Japan received one Fw 190A-5 from Germany.
The Fw 190A-5/U10 got a standard successor in the form of the Fw 190A-6. The aircraft was constructed with a somewhat lighter wing, decreasing the maximum weight to 8,600lbs. Standard armament consisted of four 20mm MG 151/20 cannon in the wings and two 7.92mm MG in the top of the nose. The table below shows the subversions of this type of which a total of 596 were built.
Subtypes Fw A-6, ?= production unknown.
- Fw 190A-6/U3: In addition to standard armament one ETC-501 rack 1,100lbs SC-500 bomb, two ETC-250 racks 550lbs SC-250 bombs or 79 gallon drop tanks. ?
- Fw 190A-6/R1: bomber killer, in addition to standard armament four 20mm MG 151/20 cannon in two WB151A nacelles. ?
- Fw 190A-6/R2: in addition to standard armament two 30mm MK 108 cannon in the center of the wings. ?
- Fw 190A-6/R3: in addition to standard armament two 30mm MK 103 cannon in the center of the wings.?
- Fw 190A-6/R4: prototype Fw 190V-45, upgraded BMW 801D-2 engine. ?
- Fw 190A-6/R6: bomber killer, in addition to standard armament two 21cm WGr. 21 rocket launchers. ?
In December 1943 production of the Fw 190A-7, a derivative of the A-5/U9 was started. In order to increase firepower, the nose guns were replaced by two 13mm MG machineguns. Of the 80 units produced, most were meant to attack enemy bombers: the A-7/R1, equipped with two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon and two 13mm MG 131 machineguns. This arsenal could be expanded by fitting two WB 151A containers beneath the wing. Both contained two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon. The table below shows the other versions.
Subtypes Fw A-7, ?= production unknown.
- Fw 190A-7/R2: in addition to standard armament two 30 mm MK 108 cannon in the wings. ?
- Fw 190A-7/R3: in addition to standard armament two 30 mm MK 103 cannon in nacelles beneath the wings. ?
- Fw 190A-7/R6: in addition to standard armament two 21 cm WGr. 21 rocket launchers beneath the wings. ?
The next version of the A series was released in December 1943. Typical for this version was the attachment point for the ETC-501 rack which had been moved further forward beneath the fuselage. The table below shows the numerous subversions.
Subtypes Fw A-8, ?= production unknown.
The final production model of the A series was the Fw 190A-9, produced simultaneously with the A-8. The aircraft was propelled by a 2,000hp BMW 801S engine. The main technical difference with the A-8 was the larger canopy. Adaptations to the armament were the same as with the A-8, causing many authors to deny this being a type in itself. These aircraft are often included in the production of the A-8.
Technical data Fw 190A-8
Definitielijst
- cannon
- Also known as gun. Often used to indicate different types of artillery.
- rocket
- A projectile propelled by a rearward facing series of explosions.
- Soviet Union
- Soviet Russia, alternative name for the USSR.
- squadron
- A military unit in the Belgian navy usually six to eight small ships operating together under one command. The smallest military unit in the Dutch air force of about 350 men. In most countries is the designation of a military unit thesize of a company. It is either an independent unit, such as a battery, or part of a bigger Calvary unit. In the air force it is the designation of a unit of aircrafts.
- torpedo
- A weapon of war. A cigar shaped body fitted with explosives and a propulsion and control mechanism. Intended to target after launch a nearby enemy ship and disable it by underwater explosion.
Fw 190B/190C
In the fall of 1942, it turned out that Great Britain had made good her disadvantage by the introduction of the Spitfire Mk IX, which triggered the need for new German fighters. It appeared that from that moment on, the Me 109 and Fw 190 fighters suffered their main disadvantage especially at great height. In order to correct this, it was decided to improve the Fw 190 by enlarging the wingspan, the application of a stronger engine and a pressurized cabin. The first at attempt at this was the Fw 190V-12. It was the first to have a pressure cabin but it was still equipped with the older A-wing and engine.
Due to the new requirements, the Fw 190B program was terminated at the sixth production model of the B series. By using a new engine, the Daimler-Benz DB 603, the length of the plane grew with 26". The first prototype of the new series was the Fw 190V-13 which was equipped with a new 1,750 hp DB 603-E engine. The V-15 and V-16 were identical but the V-16 was equipped with a new 1,800hp DB 603E engine, raising the maximum speed to 451mph. The next prototype received a pressure cabin, an enlarged horizontal tailplane and a four-blade airscrew driven by a DB 603-G.
Between 1943 and early 1944 these and other prototypes were tested extensively. This led to two production models, the Fw 190C-1 without and the Fw 190C-2 with a pressure cabin. Wingspan of the aircraft was 40ft, wing surface was 217sqft. Armament consisted of two 13mm MG 131 machineguns on the nose, four MG 151/20 cannon in the wings and one cannon firing through the hollow axle of the air screw. A total of nine units of the C series were built but problems with the pressure cabins kept popping up so the C program was canceled.
Definitielijst
- cannon
- Also known as gun. Often used to indicate different types of artillery.
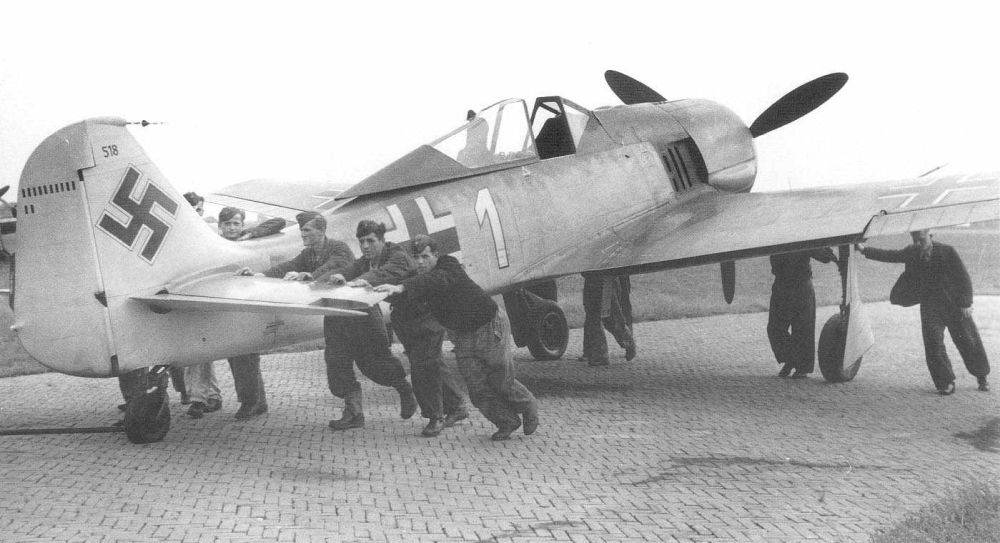
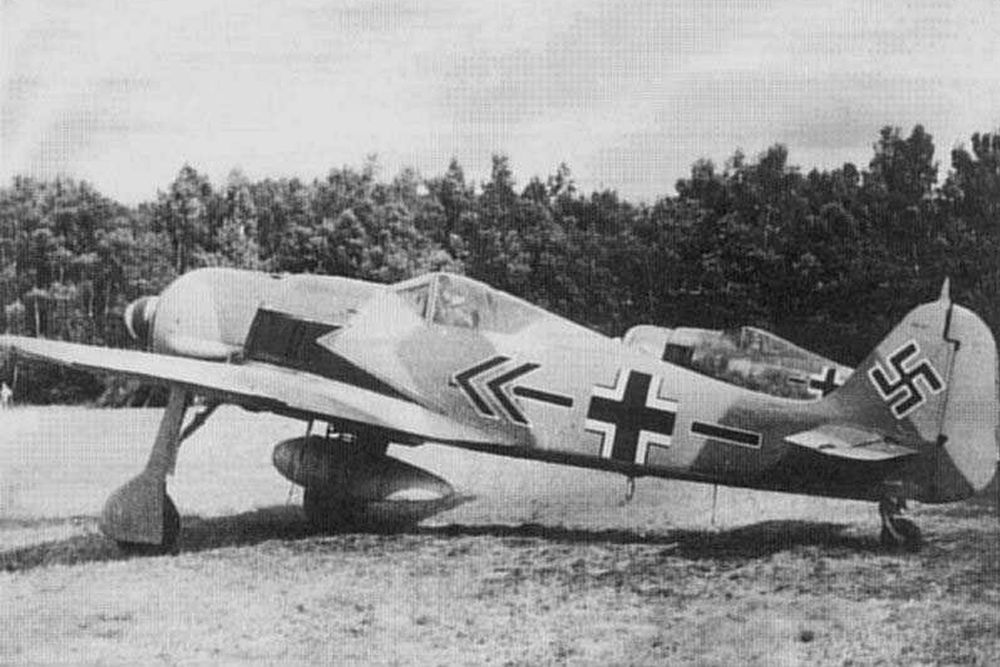
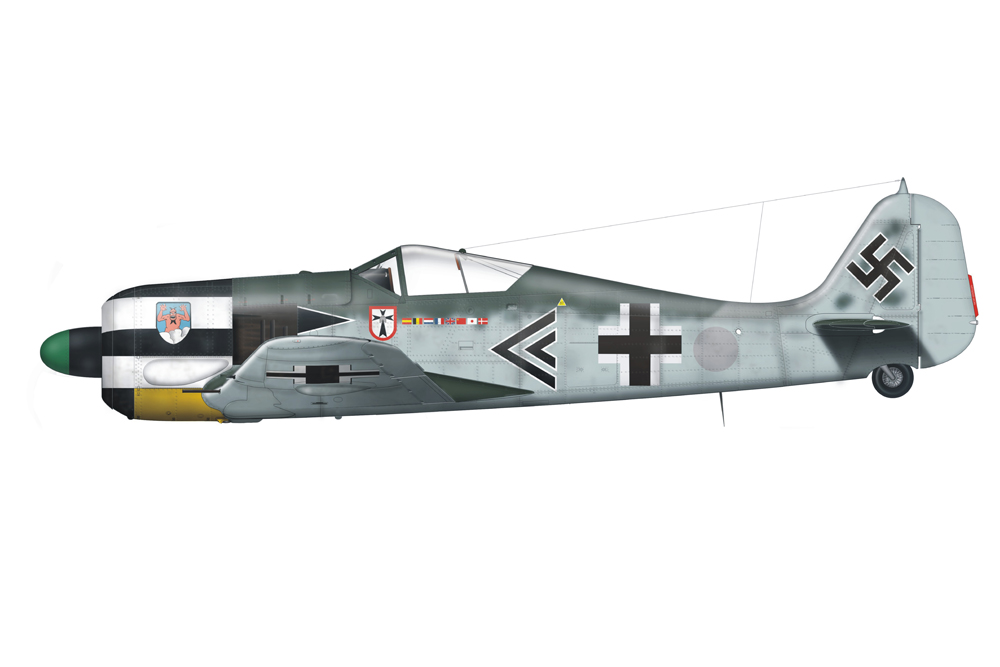
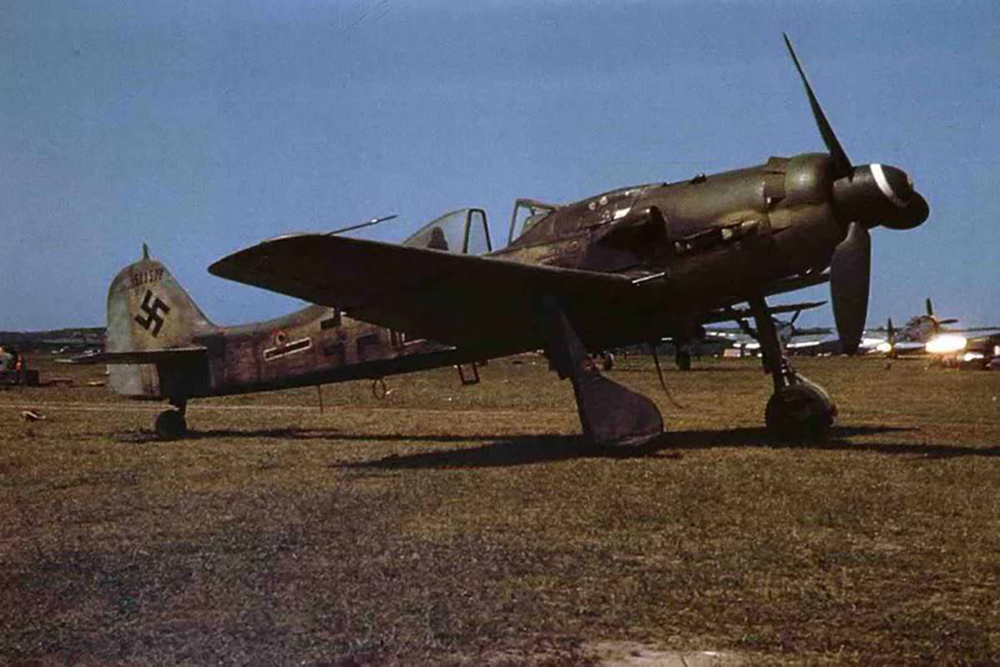
Fw 190D
Meanwhile, the D series had entered production. This version turned out to perform excellently. Development of the Fw 190D progressed in addition to the development of the B and C series. The first prototype, the Fw 190V-17 was an 190A-0 equipped with a 1,750hp Junkers Jumo 213-1001-S engine, a pressurized cabin and a wingspan of 40ft. Equipped with a Jumo 213A-1 engine this aircraft became the Fw 190V-17/U1 with a lengthened fuselage, 2ft added to the front and 1,6ft to the rear to enhance stability.
This aircraft made its maiden flight in May 1944 and gave much satisfaction. It was followed up with various prototypes with different armament until eventually the first pre-series of 10 Fw 190D-0 could be produced. As the D series was based on the Fw 190A-8, it was decided to continue the numbering in sequence and so, the first production version became the Fw 190D-9. The D-9 was based on the frame of the A-8 with a 2,240hp Jumo 213 engine. Standard armament consisted of two 13mm MG 131 machineguns on the nose, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon in the wings and an ETC-504 rack beneath the fuselage for a 550lbs SC 250 bomb or a 79 gallon drop tank. The first units entered service in the fall of 1944 in III/JG 54, tasked with protecting the test base of the new Messerschmitt Me 262 jet fighters. In October, they entered service in I/JG 26. The only subversion produced was the Fw 190D-9/R11, an all-weather fighter equipped with a PKS 12 navigation device. The D-10 has not been produced and only seven prototypes of the D-11 have been constructed. Therefore, the next version is the Fw 190D-12 ground attack fighter. This version, produced in February/March 1945 was equipped with a 1,750hp Junkers Jumo 213F. Because the war was almost over, only a few units of this type have been built.
Just like the other versions of the FW 190, there have been no orders for export of this aircraft. It is known however that during the Soviet invasion of Eastern Prussia, various aircraft have been captured. Subsequently, these aircraft entered service in the Red air force. In any case, it is certain that at least one regiment has been established with these aircraft within the air force of the Baltic Fleet.
Technical data Fw 190D-9
- Task: fighter/fighter bomber
- Crew: 1
- Wingspan: 35ft
- Surface: 197sqft
- Length: 339ft
- Heigth: 11ft
- Weight empty/max: 7,010/10,692lbs
- Engine: 12 cylinder 1,770hp Junkers Jumo 213AB
- Speed max/cruise: 426/?mph
- Range: 6,214 miles
- Ceiling: 32,808ft
- Armament: two 13mm MG 131, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon, 550lbs bombs
- Produced: 674
Definitielijst
- cannon
- Also known as gun. Often used to indicate different types of artillery.
- invasion
- Armed incursion.
- regiment
- Part of a division. A division divided into a number of regiments. In the army traditionally the name of the major organised unit of one type of weapon.
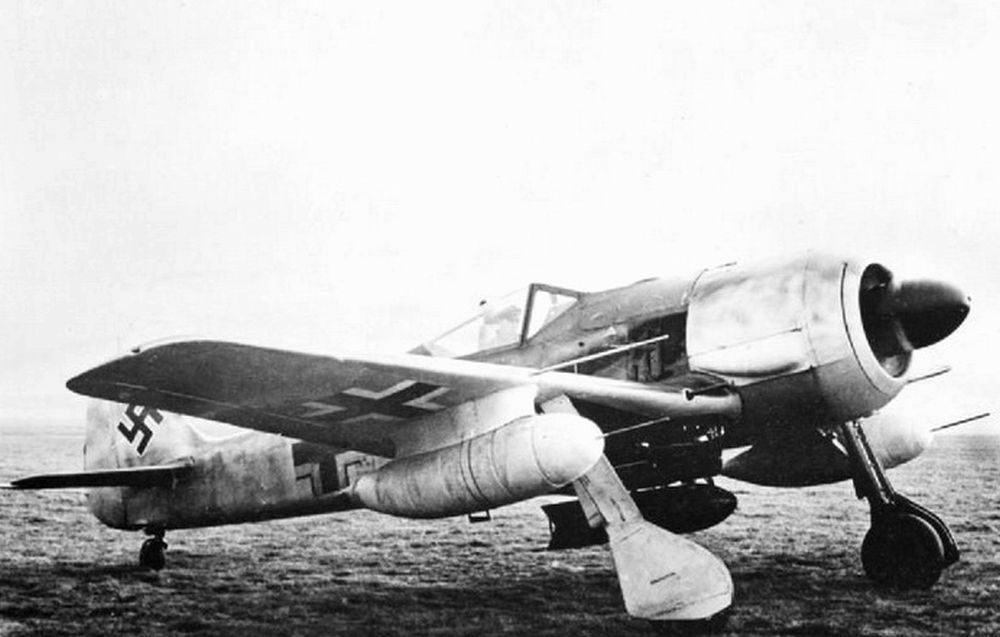
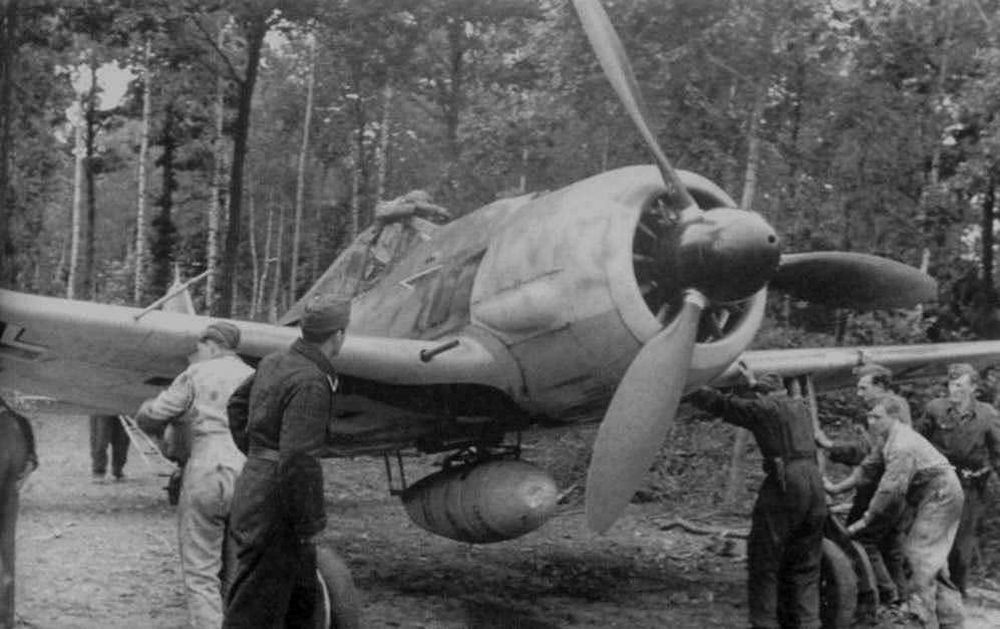
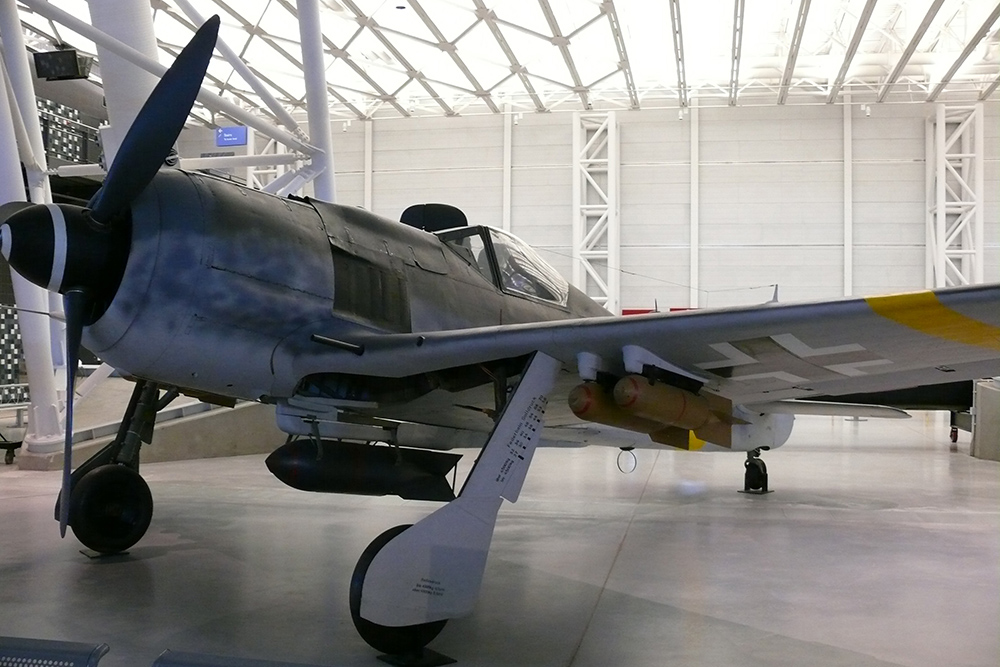
Fw 190F
It had soon turned out that the concept of the Fw 190 was perfectly suitable for more tasks than just a fighter aircraft. Specifically focused on a certain target, the Fw 190F ground support fighter and the Fw 190G fighter-bomber were developed, Both versions became in fact more of an attack aircraft than a fighter. The Fw 190F was developed from the Fw 190A-5/U3 of which the landing gear was strengthened and the standard equipment was augmented by fixing an ETC-501 rack beneath the fuselage and four ETC-50 racks beneath the wings. In order to achieve better protection while carrying out their tasks, the planes were fitted with stronger armor. concentrated on the belly for pilot, engine and fuel.
Between 25 and 30 aircraft of the first model, the Fw 190F-1, were produced mainly for the purpose of training and testing. The first real production model, based on the frame of the FW 190A-5 was the Fw 190F-2 of which 271 units were produced. This version was identical to the F-1 except for the canopy which offered a better view. An ER-4 rack could be fitted to the ETC-501, enabling the aircraft to carry 990lbs of SC-50 bombs (99lbs each). Some of these aircraft were fitted out as Fw 190F-2/Trop for use in Tunisia and southern Italy.
At the Arado works, some 250 aircraft were built based on a Fw 190A-6, the Fw 190F-3. The only difference from the A-6 was that instead of four ETC-50 racks, two ETC-250 racks were fitted so two 550lbs SC-250 bombs or two 79 gallon drop tanks could be carried. The table below shows the two known versions.
Subversions Fw 190F
- Fw 190F-3/R1: equipped with a simple bomb aiming device
- Fw190F-3/R3: tank destroyer with two 30mm Mk 103 cannon in nacelles beneath the wings.
Subversions Fw 190F-8/U1
- Fw 190F-8/U1: two-seat trainer, converted 190s, only a few delivered
- Fw 190F-8/U2: equipped with a 881lbs BT-400 or 1,543lbs BT-700 torpedo
- Fw 190F-8/U3: equipped with a 3,086lbs BT-1400 torpedo
- Fw 190F-8/U14: equipped with a LT F5b torpedo
- Fw 190F-8/U15 equipped with a 2,094lbs BT-900 torpedo
- Fw 190F-8/R1: two 13mm MG 131 in the nose, four MG 151/20 cannon in the wings and four ETC-71 bomb racks
- Fw 190F-8/R2: two 13mm MG 131 in the nose, two MG 151/20 cannon in the wings and two 30mm MK 108 cannon in nacelles
- Fw 190F-8/R3: two 13mm MG 131 in the nose, two MG 151/20 cannon in the wings and two 30mm MK 108 cannon to destroy tanks
- Fw 190F-8/R5: long range version of the F-8/R3, never built
- Fw 190F-8/R13: night fighter/ground support with additional navigation equipment, two 13mm MG 131 in the nose, max bombload 3,307lbs on one ETC-501 and two ETC-503 bomb racks
- Fw 190F-8/R14: torpedo bomber, BMW 801TU engine, PKS 12 navigation, two MG 151/20 cannon, one LT 5b torpedo on a ETC-502 rack
- Fw 190F-8/R15: torpedo bomber based on the F-8/R14 with BMW 801 D-2 engine , one 3,086lbs LT -1400 torpedo
- Fw 190F-8/R16: torpedo bomber based on the F-8/R15, one 1,543lbs LT -700 torpedo
In addition, a limited number of aircraft was delivered with 24 55mm R4-M rockets, 14 220lbs RBS.B/21 rockets, 2 clusters of 280mm WGr. 28 rockets etc. Production of the Fw 190F-8 ran parallel to the Fw 190FG-9 with an even stronger armor and a 2,000hp BMW 601TS/TH engine. Eventually, only a few were built. Furthermore, production of the Fw 190F-1 to F-17 was planned but not built because the war ended.
Technical data Fw 190F-3
- Task: ground support fighter
- Crew: 1
- Wingspan: 354ft
- Wing surface: 197sqft
- Length: 29ft
- Height: 13ft
- Weight: ?
- Engine: 1,700hp BMW 801D-2
- Speed: max 635mph, cruise ?
- Range: 466 miles
- Ceiling: 34777ft
- Armament:two 13mm MG 131, two 20mm MG 151/20 cannon, 220lbs bombs
- Production: +/- 250
Definitielijst
- cannon
- Also known as gun. Often used to indicate different types of artillery.
- destroyer
- Very light, fast and agile warship, intended to destroy large enemy ships by surprise attack and eliminating them by using torpedoes.
- torpedo
- A weapon of war. A cigar shaped body fitted with explosives and a propulsion and control mechanism. Intended to target after launch a nearby enemy ship and disable it by underwater explosion.
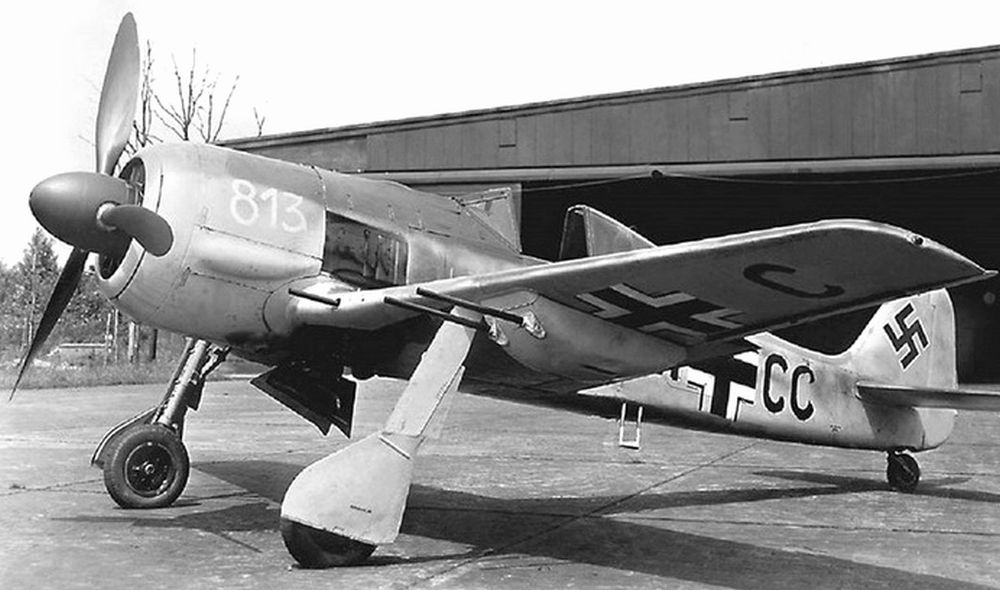
Fw 190G
Because of its much simpler construction, the Fw 190G entered production before the Fw 190F. The aircraft was based on the Fw 190A-4/U8 and the A-5/U3 in which the nose guns had been omitted to save weight. For its own defense, only two 20mm MG 151/20 had been left.
Of the pre-series, the Fw 190G-0 only a few were built. They were equipped with a ETC-501 rack beneath the wings, adapted to carry either a 1,102 SC-500 or a 2,204 SC-1000 bomb. The first production model, the Fw 190G-1, of which 49 were built, was based on the Fw 190A-4. It was identical to the Fw 190G-0. The landing gear was strengthened in a way to enable the aircraft to carry a 3,968lbs bomb. A standard two 79 gallon drop tanks were fitted beneath the wings. The 1,700hp BMW 801D-2 was shortened, decreasing the length to 29ft.
The first unit to receive the only version of the aircraft, Fw 190G-1/Trop, was the II/Schlachtgeschwader 2 in North-Africa. It was delivered between February and May 1943. A number of these planes later saw service in Italy in Schlachtgeschwader B(SG) 4. Most of the aircraft though were sent to the Eastern Front where they were first deployed by I and II/SG 1 during the Battle of Kursk in June 1943. Furthermore they served in SG 2, 4, 5 and 10 at that front.
Based on the frame of the Fw 190A-5, 468 Fw 190G-2s were produced. The nose was slightly longer again, increasing the length to 29ft. By using Messerschmitt racks beneath the wings, tanks could be fitted increasing the range of the aircraft to 963 miles. A few of these planes were built as Fw 190G-2/Trop for use in North-Africa and the southern Soviet Union.
From October 1943 onwards, an unknown number of FW 190G-3s was produced. This was in fact a G-2 with a PKS 11 auto pilot and Focke Wulf bomb racks. A few planes were built as G-3/Trop and the only known subversion is the Fw 190G-5 with four ETC-50 racks for 110lbs SC-50 bombs. This G-3 fathered an unknown number of Fw 190G-4 aircraft, fitted with three ETC-503 bomb racks. The G-5 and 6 were not built and the FW 190G-7 is only known as a test aircraft for a torpedo shaped 238 gallon external fuel tank. The last production model was the Fw 190G-8.
Based on a 190A-8 frame, an unknown number of planes has been produced between September 1943 and February 1945. Best known versions are the Fw 190G-8/R4 with a GM I upgrade of the BMW 801D-2 engine and a version with a 2,000hp BMW 801TV engine and four ETC-50 bomb racks, apart from the already present ETC-501, the Fw 190G-8/R5.
Technical data Fw 190G-3
- Task: fighter-bomber
- Crew: 1
- Wingspan: 34ft
- Wing surface: 197 sqft
- Length: 29ft
- Height: 13ft
- Weight: ?
- Engine: 1,700hp BMW 801D-2
- Speed: max 388/cruise 262mph
- Range: 522/652 with drop tanks
- Ceiling: ?
- Armament: two 20mm MG 151/20, 3,968lbs bombs
- Production: ?
Definitielijst
- Soviet Union
- Soviet Russia, alternative name for the USSR.
- torpedo
- A weapon of war. A cigar shaped body fitted with explosives and a propulsion and control mechanism. Intended to target after launch a nearby enemy ship and disable it by underwater explosion.
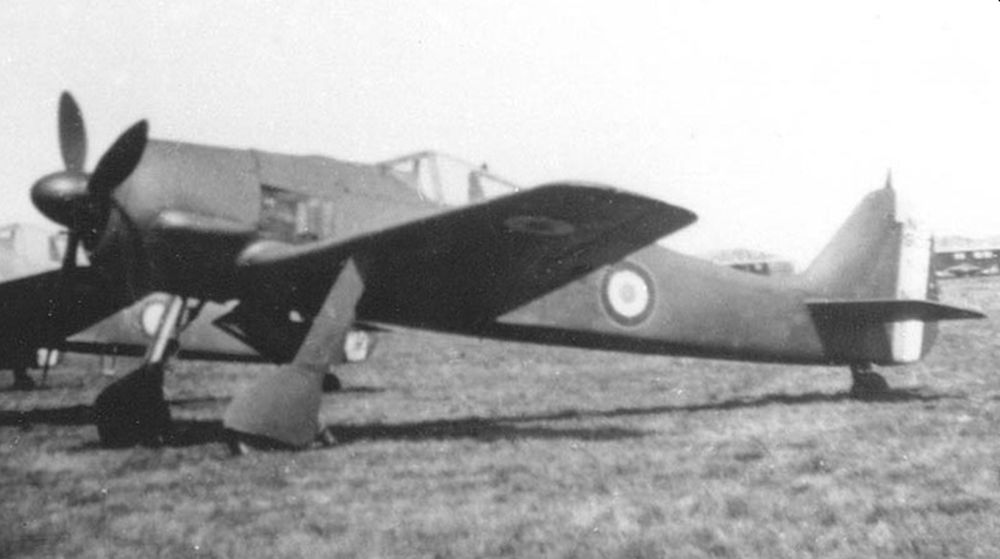
Fw 190S/SNCAC NC.900
In addition to all converted aircraft for flight training, 58 Fw 190S two-seat trainers were built. They were equipped with an extended cockpit with dual controls.
After the war, the French aviation industry has produced its own version of the Fw 190, the SNCAC NC.900 for a few years, destined for the French air force and of which 64 have been delivered.
Information
- Article by:
- Wilco Vermeer
- Translated by:
- Arnold Palthe
- Published on:
- 13-12-2023
- Last edit on:
- 22-06-2024
- Feedback?
- Send it!