Nieuwste artikelen
- Article by Michiel Stinckens
- Published on December 25th, 2023
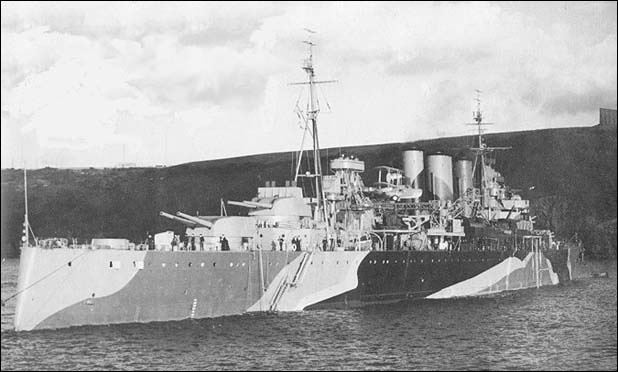
British heavy cruisers of the Kent Class
The vessels of the Kent class were constructed in the late 20s to compensate for the lack of warships in the Pacific and the Chinese Sea. As the Admiralty paid no attention to the threat from the air, only a little anti-aircraft defense was installed. This was a severe shortcoming as in the end, out of these seven vessels, two were sunk by Japanese aircraft. Halfway through the 30s, it was decided to equip them with additional AA artillery but this proved insufficient. This didn't mean they didn't prove to be valuable vessels during World War Two. Although they were already outdated at the time, both the British and Australians put these ships to good use.
- Article by Wilco Vermeer
- Published on December 13th, 2023
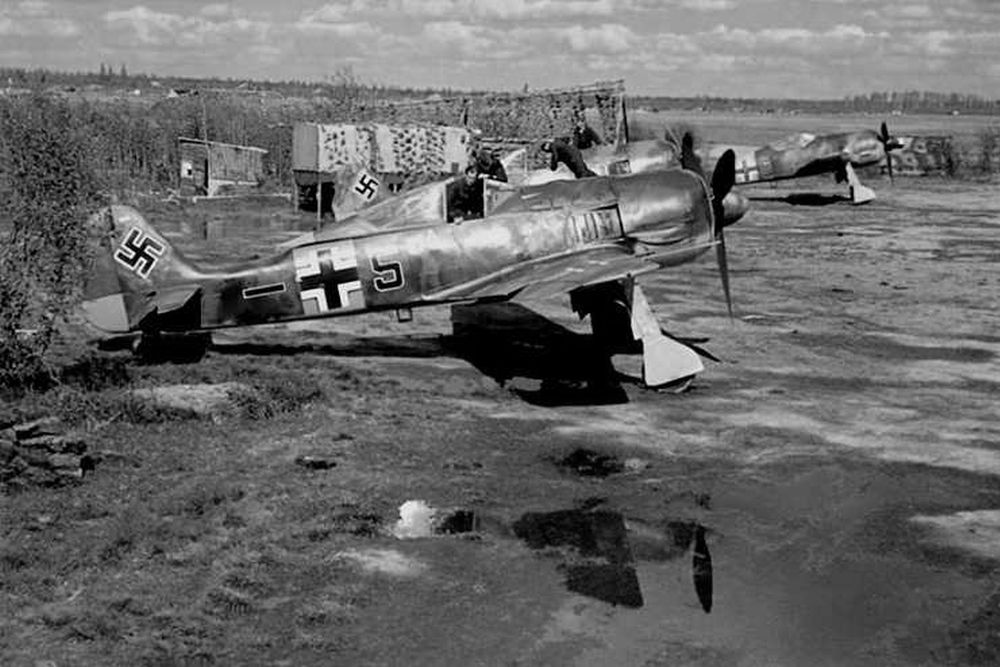
Focke Wulf Fw 190
In addition to the Messerschmitt Bf 109, the Focke Wulf Fw 190 belongs to the most important fighter aircraft of the Luftwaffe during World War Two. When the Fw 190 entered service in 1941, it could rightfully claim the title best fighter in the world. It performed far better than the best Allied fighter of the day, the Supermarine Spitfire Mk V. More than a year later, a new generation of Spitfires, the Mk IX, would match the Fw 190. After that time, this fighter was an even match for the best Allied fighters due to its excellent adaptability.
- Article by Wilco Vermeer
- Published on November 28th, 2023
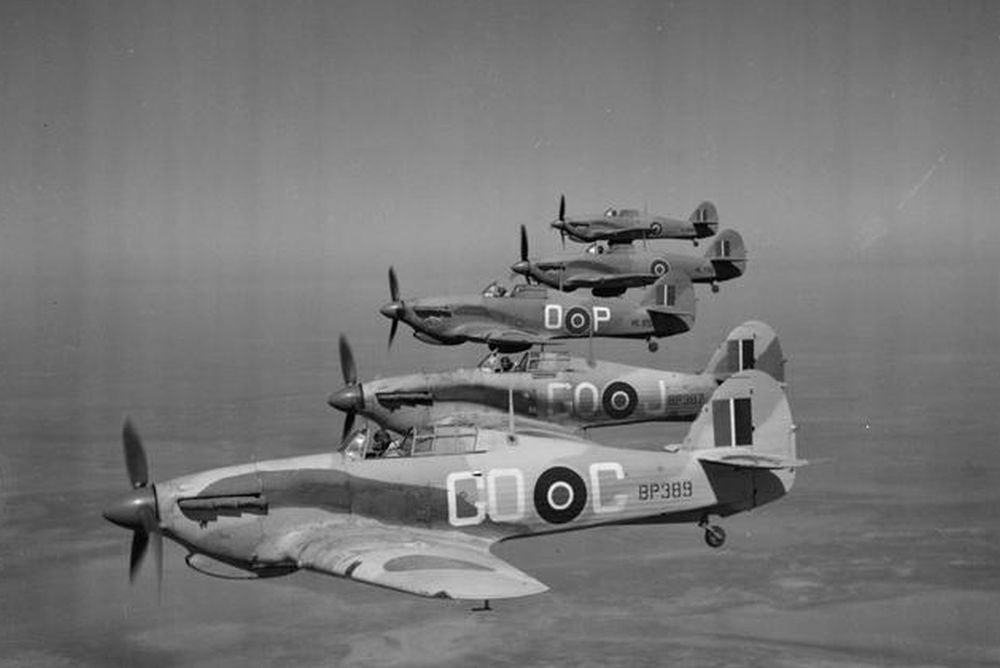
Hawker Hurricane
The British victory after the Battle of Britain is usually attributed to the legendary Supermarine Spitfire. Honesty compels to mention though that during this battle, the majority of the RAF squadrons hadn't been equipped with the Spitfire yet but with the Hawker Hurricane. This successful airplane, of which over 15,000 have been delivered between 1937 and 1944, saw action on almost all battlegrounds of WW2.
- Article by Frank van der Drift
- Published on September 29th, 2023
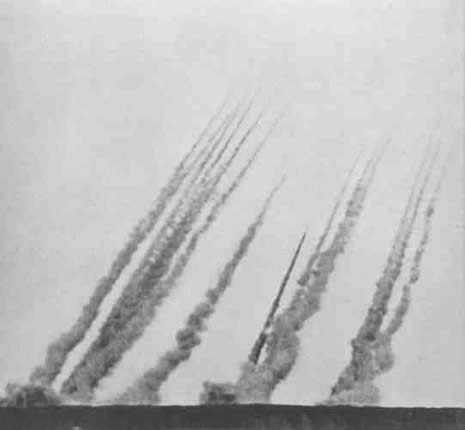
German Rocket Artillery
Using rocket technology to launch projectiles was already possible during the First World War. Previously, the possibility was there but projectiles were unpredictable during launch as well as in flight and hence they were never use in practice. During the 20s and 30s, experiments were conducted with fuels and materials. Pursuant to the Treaty of Versailles however, Germany was forbidden to develop long range artillery and so these experiments were either conducted in secrecy or in foreign countries.
- Article by Wilco Vermeer
- Published on September 9th, 2023
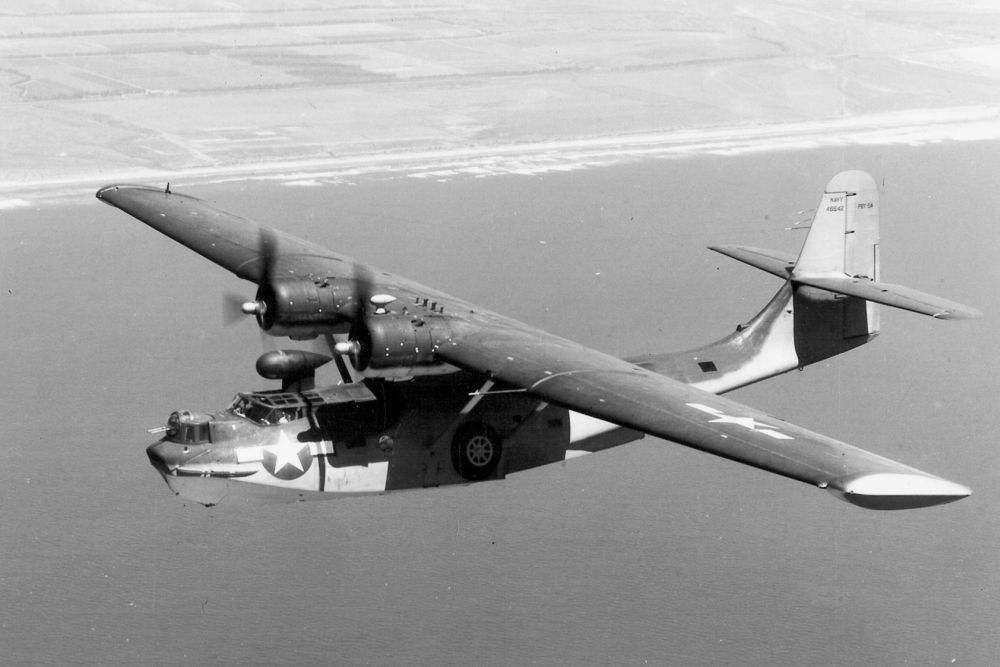
Consolidated PBY Catalina
No other flying boat has become so well-known and popular as the Consolidated Catalina, affectivle known as the Cat. Until long after World War Two, many navies and air forces of various countries have flown the type. The Catalina has gained enormous familiarity and popularity by its diversity, simplicity and ease of handling which lasts until this day.
- Article by Wilco Vermeer
- Published on September 2nd, 2023
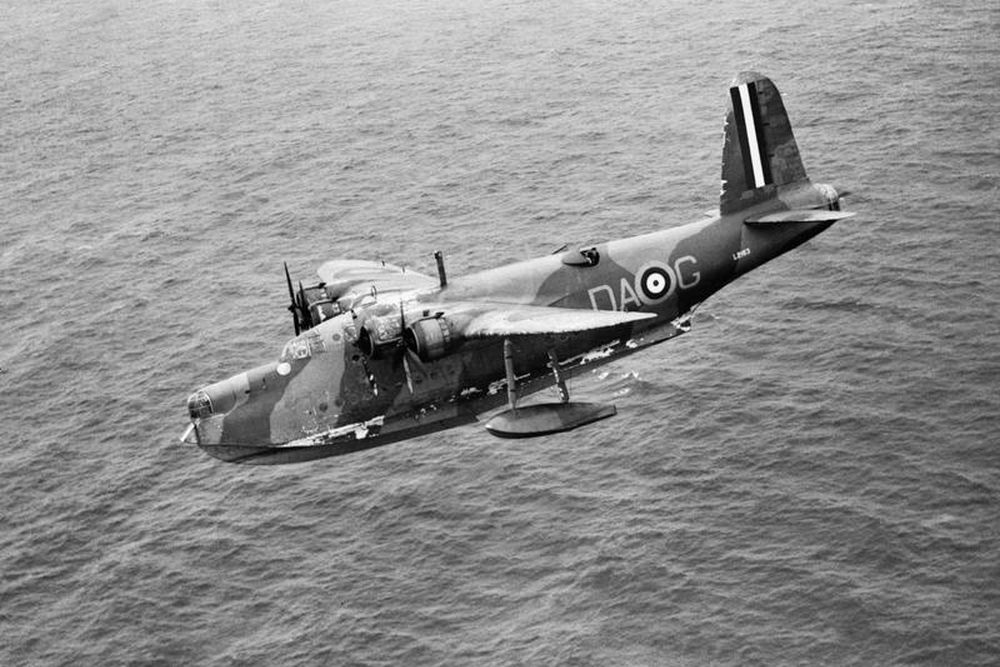
Short Sunderland
The Short Sunderland was a direct derivative of the civil Short Empire seaplanes of Imperial Airways.They were a formidable gun platform which brought fear to U-boat commanders and attacking German aircrews alike. The latter called respectfully called it 'Das fliegende Stachelschwein'.
- Article by Frank van der Drift
- Published on August 27th, 2023
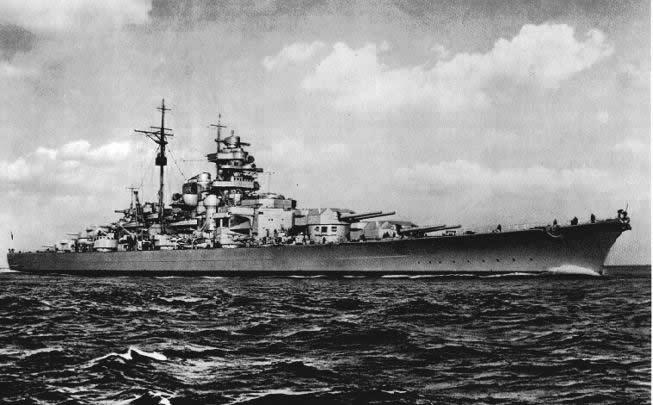
German Battleships Bismarck class
Designing the Bismarck started as early as 1934 and entailed a 35,000 BRT so-called Panzerschiff or armored vessel equipped with 8 38cm guns. The design entailed an armor strong enough to withstand any battleship and the armament was sufficiently strong to take on any opponent. Final design was completed in May 1935
- Article by Peter Kimenai
- Published on August 23rd, 2023
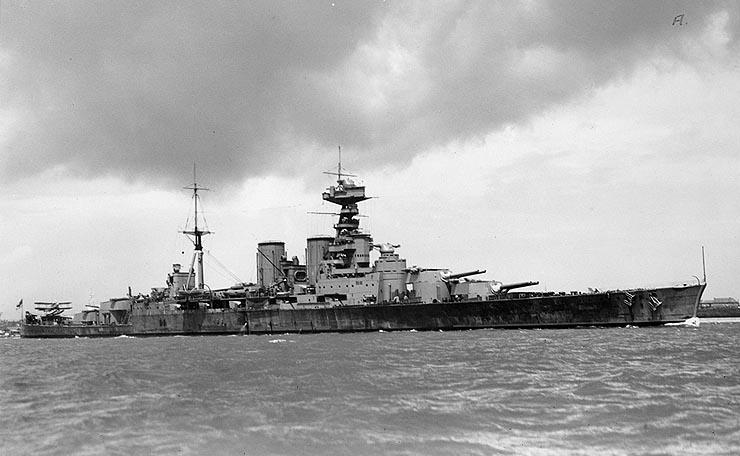
British battlecruisers: HMS Hood
Mighty Hood, that is how the British called HMS Hood in the interbellum. During that period, she was indeed the largest battleship in the world and the British were proud of their symbol of maritime military power. The vessel strongly appealed to the imagination by her fire power, speed and dimensions in a period in which the British population felt a strong affinity towards the Royal Navy.
- Article by Peter Kimenai
- Published on August 14th, 2023
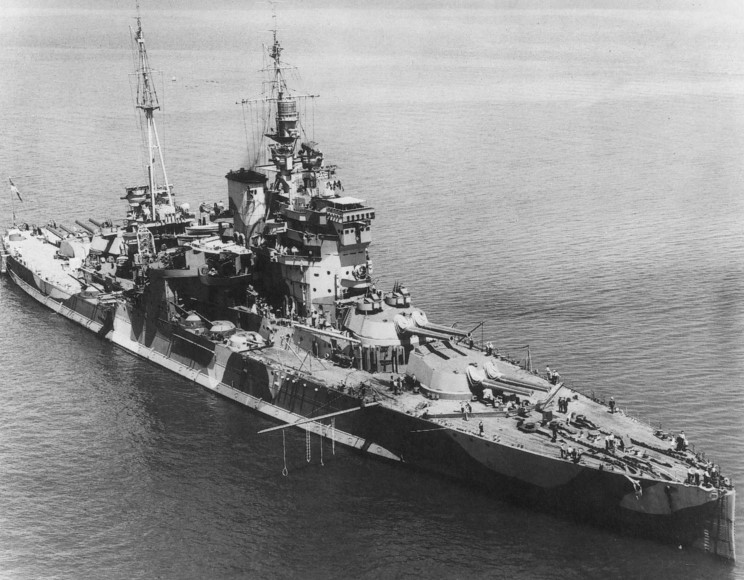
British battleships of the Queen Elizabeth class
On the eve of World War Two, Great Britain had 12 capital ships and 3 battlecruisers at her disposal. Right after World War One, this number stood at 46. The Washington Treaty, signed in 1921 by the major naval powers at the time in order to prevent a new arms race, stipulated that in the 20s, 28 British warships be dismantled. The five Queen Elizabeth class vessels and the five of the Royal Sovereign class were retained.