-
01-01-1943: From January onwards, U-boats mainly operate in the central Atlantic and along the northern coast of South-America. The R.A.F. starts heavy bombardments on U-boat bases along the Gulf of Biscay.
-
01-01-1943: Soviet forces recapture Wlikiye Luky and Elista south of Stalingrad and Tsjikola in the Caucasus.
-
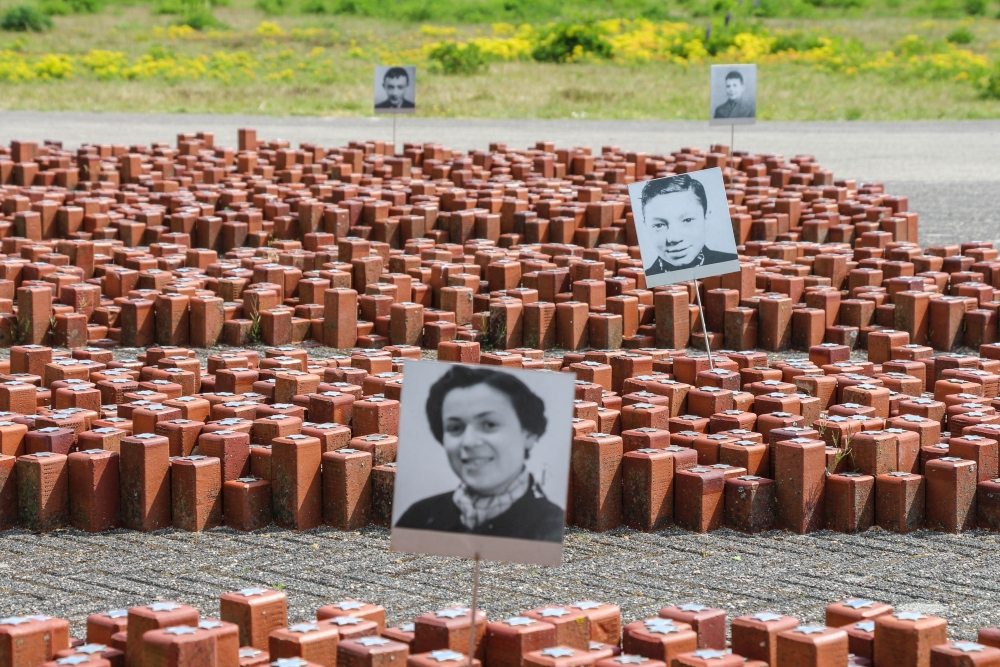
01-01-1943: Early 1943, camp Amersfoort is designated as penal camp for those refusing employment and those who breach their contract.
-
01-01-1943 - 01-01-1943: Operation White by German and Italian troops against Tito’s partisans.
-
02-01-1943: The Germans start withdrawing from the Caucasus.
-
02-01-1943: Japanese resistance near Buna on New Guinea is finally broken.
-
03-01-1943: The Soviets recapture Malgovek and Mosdok in the Caucasus.
-
04-01-1943: Soviet units occupy Tsjernysjkovski southwest of Stalingrad and Naltsjik in the Caucasus.
-
04-01-1943: First illegal action against a Central Register of Population in Wageningen.
-
08-01-1943: Rokossovski sends General Paulus an ultimatum to capitulate. Hitler forbids capitulation.
-
09-01-1943: China (Nanking) declares war on Great Britain and the United States.
-
10-01-1943: Soviet troops launch a massive offensive against the Germans in Stalingrad.
-
10-01-1943: The Americans start their final and largest offensive on Guadalcanal.
-
11-01-1943: The Soviets recapture Georgievsk, Mineralnye, Wody, Piatigorsk and Budenovsk in the Caucasus and Ketelnikovo and Koberle in the southern Don-sector.
-
11-01-1943: In Paris, Sauckel demands 250,000 French workers before March 15.
-
11-01-1943: The governments of Great Britain and the United States sign an agreement with Chang Kai Chek, ceding all extraterritorial rights.
-
13-01-1943: Hitler issues a decree with instructions for waging total war.
-
13-01-1943: Camp Herzogenbusch near Vught is commissioned.
-
14-01-1943 - 14-01-1943: Roosevelt and Churchill meet in Casablanca where the decision is made to demand unconditional surrender of the Axis powers. Plans for an invasion of Sicily and in western Europe are postponed for a year.
-
15-01-1943: The British 8th Army launches an offensive against Buerat in Tripolitania.
-
15-01-1943: German authorities in the Netherlands are to make 22,000 metal workers available for employment in Germany before March 10. Stahl und Eisenaktion. In addition, 78,000 unschooled workers have to be delivered.
-
16-01-1943: Iraq declares war on Germany, Italy and Japan.
-
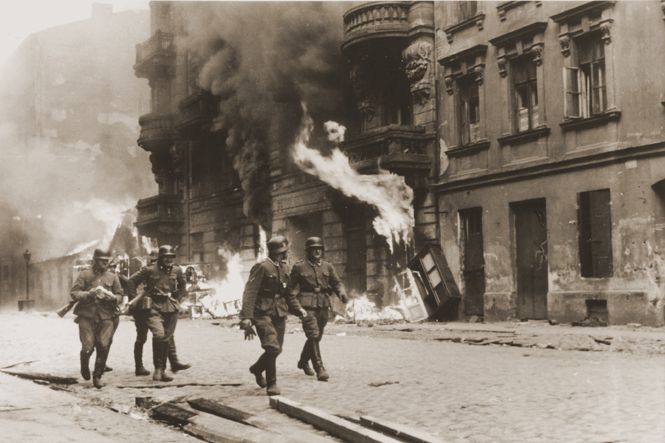
18-01-1943: Inhabitants of the ghetto in Warsaw, Poland, start a revolt.
-
18-01-1943: Soviet troops recapture a 10 mile wide corridor south of Lake Ladoga, breaking the German siege of Leningrad.
-
18-01-1943: Soviet units recapture Tsjerkessk, Divnu and Kaimenka in the Caucasus.
-
18-01-1943: The Germans attack British and French near Bou Araba in Tunisia.
-
19-01-1943: On the Voronezh front, the Soviets occupy Waluki and Urazavo.
-
19-01-1943: In Ottawa Princes Margriet is born.
-
20-01-1943: The Belgian R.A.F. pilot Jean de Sélys-Longchamps attacks Gestapo headquarters in Brussels on his own. Four Germans are killed and the building sustains severe damage.
-
21-01-1943: The Soviets recapture Vorosjilovsk in the Caucasus.
-
22-01-1943: Japanese resistance at Sanananda on New Guinea collapses; it is the first Allied victory on land in the Pacific.
-
23-01-1943: The British 8th Army commanded by Montgomery captures Tripoli in Libya.
-
23-01-1943: After an arduous journey from Chad, the division of French general Leclerc joins Montgomery’s 8th Army in Libya.
-
24-01-1943: The Soviets capture Starobjelsk in the Donets basin.
-
27-01-1943: The first American bombardments on Germany (Wilhelmshafen).
-
27-01-1943: In Germany all men between the ages of 16 and 65 and all women between the ages of 17 and 45 are obliged to report for duty in the defense of the Reich.
-
28-01-1943: The Soviets take Voronezh.
-
29-01-1943: Decree to the effect that all Gypsys must be arrested and deported to an extermination camp.
-
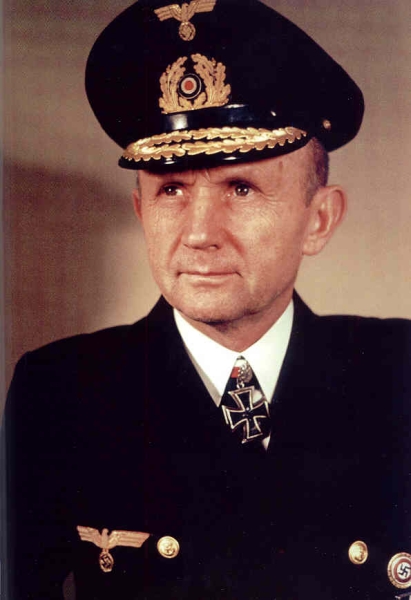
30-01-1943: Grossadmiral Raeder is succeeded by Admiral Dönitz as Supreme Commander of the Kriegsmarine.
-
30-01-1943: The Soviets recapture Majkop in the Caucasus.
-
30-01-1943: The Adana conference: meeting between Churchill and Turkish president Inönü.
-
31-01-1943: Paulus, only recently promoted to Feldmarschall, surrenders in the southern sector of Stalingrad.
-
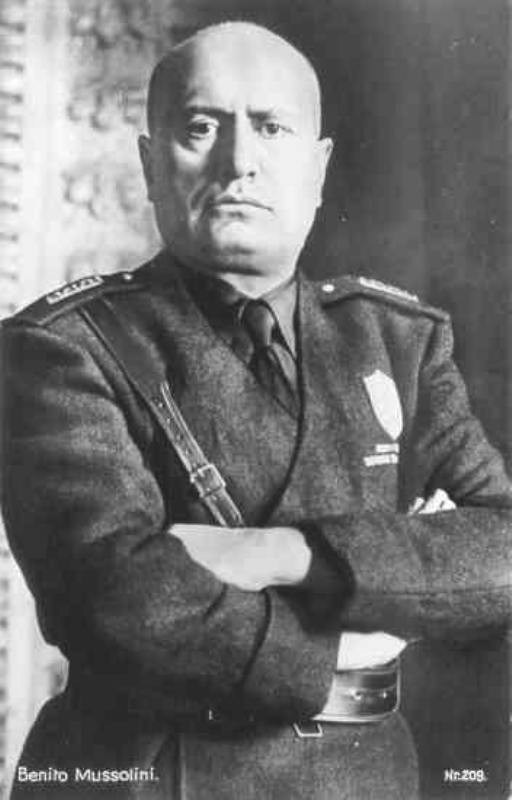
31-01-1943: Mussolini fires his chief of staff Cavallero and names General Vittorio Ambrosio his successor.
-
31-01-1943: In Meppel, the first issue of the paper Trouw is published.
-
01-02-1943: Mussert forms a Department of State.
-
01-02-1943: Japan starts to evacuate Guadalcanal.
-
02-02-1943: German troops in the northern sector of Stalingrad surrender; 90,000 men become prisoners-of-war. It is Hitler’s first major defeat in Europe.
-
02-02-1943: American troops cross the mouth of the river Bonegi near Tassafaronga on Guadalcanal.
-
03-02-1943: Churchill visits the British army in Tripoli.
-
04-02-1943: Forward units of the British 8th army advance into Tunisia.
-
05-02-1943: General Seyffardt is shot by Jan Verleun, member of CS VI.
-
05-02-1943: Mussolini fires his Secretary of Foreign Affairs, Count Ciano and takes the post himself. Ciano becomes Ambassador to the Vatican. The Italian cabinet is reorganized.
-
06-02-1943: Rounding up of students in Amsterdam, Utrecht, Delft and Wageningen. Many students go into hiding. Universities are closing down.
-
07-02-1943 - 07-02-1943: Japanese troops evacuate Guadalcanal. The Americans occupy the northwestern corner of the island.
-
08-02-1943: Soviet troops recapture the city of Kursk.
-
08-02-1943: British-Indian troops launch a guerilla war against the Japanese troops in Burma.
-
09-02-1943: Bombing attack on a train near Zaventem, Belgium carrying soldiers on leave.
-
09-02-1943: End of organized Japanese resistance on Guadalcanal.
-
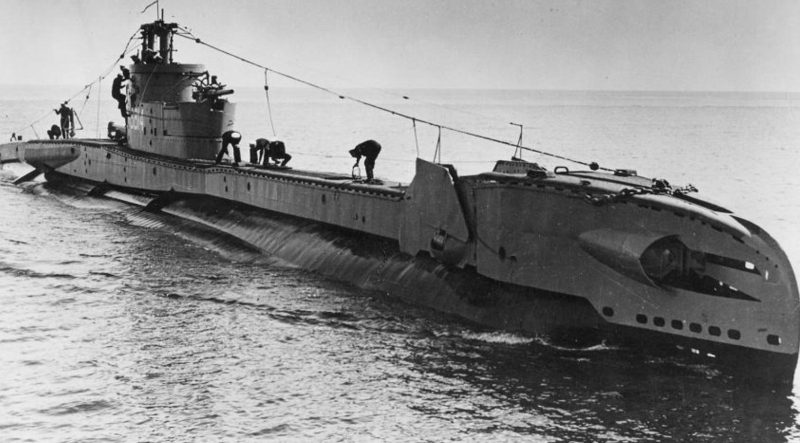
09-02-1943: The Dutch submarine H.M. Dolfijn sinks the Italian submarine Malachite.
-
09-02-1943: Murder attempt on the Secretary-general of People’s Education and Arts, H. Reydon and his wife by H. Kastein, member of the group CS VI.
-
09-02-1943: Second rounding up. Arrest of "sons of plutocrats" selected by the N.S.B.
-
10-02-1943: Jewish orphans from Amsterdam are deported to Poland.
-
12-02-1943: Krasnodar is recaptured by the Soviets.
-
14-02-1943: German troops launch a strong counter offensive to the west from the Faïd pass in Tunisia.
-
14-02-1943: Soviet troops recapture Rostov on the Don and Vorosjilovgrad.
-
14-02-1943: Parachuting at Kallenkote from MI9 agent Trix Terwindt. She is the only woman who falls into German hands as part of the Englandspiel.
-
14-02-1943 - 14-02-1943: The battle of the Casserine Pass in North-Africa between the American 2nd Corps and the German Afrika Korps.
-
15-02-1943: Kharkov is temporarily recaptured by the Red Army.
-
16-02-1943: The British 8th Army captures German outposts on the Mareth line.
-
17-02-1943: The joint churches protest to Seyss-Inquart about the growing lawlessness. (See February 21).
-
17-02-1943 - 17-02-1943: In France, people born in 1920, 1921 and 1922 are called up for mandatory employment, End of the second Sauckel action in France.
-
18-02-1943: Students Hans and Sophie Scholl and Christoph Probst are arrested in Munich University. The end of their underground activities by their resistance group Die Weisse Rose (White Rose) in Munich.
-
18-02-1943: Joseph Goebbels proclaims total war in his famous speech in the Sportpalast in Berlin: "Nun, Volk, steh auf und Sturm brich los" (Now people, stand up and storm break loose).
-
20-02-1943: German armored units break through the El-Qassarin pass and reach Thala and Tébessa.
-
21-02-1943: The protest from the churches is read from the pulpit. (See February 17).
-
21-02-1943: Hans and Sophie Scholl and Christoph Probst are beheaded.
-
21-02-1943: American troops go ashore on Russell island.
-
22-02-1943: The German Army group Don, commanded by Von Manstein launches a counter offensive but fails to trap the Soviets in pockets.
-
25-02-1943: Formation of the Indochinese Democratic Front by the Vietminh.
-
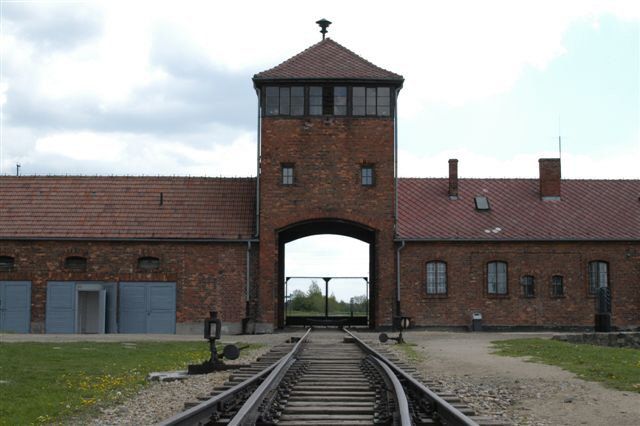
25-02-1943: Arrival of the first Gypsy transport from Germany in Birkenau.
-
25-02-1943: The El-Qasserin pass is back in Allied hands.
-
26-02-1943 - 26-02-1943: German units commanded by General Jürgen von Arnim attack British troops in northern Tunisia. The British are gradually pushed back to Medjez and Béja.
-
27-02-1943: Soviet troops recapture Pavlograd. German troops recapture Lozovaya.
-
27-02-1943: Jews who were employed in the armaments industry in Berlin are deported to Auschwitz.
-
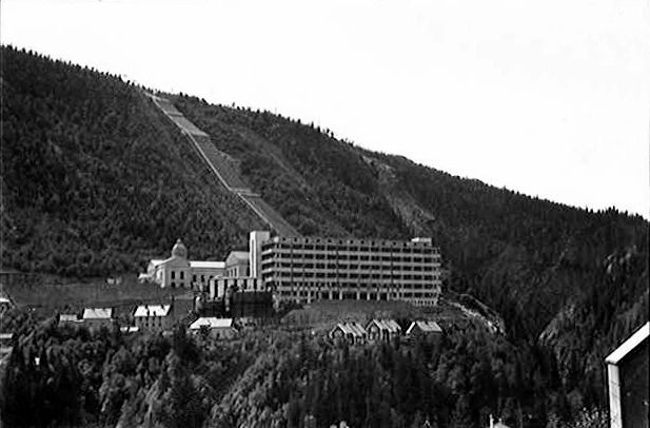
28-02-1943: In a special S.O.E. operation, carried out by 9 agents and six Norwegian resistance fighters, extremely severe damage is inflicted on the Norsk Hydro Elektrisk plant at Wimork. This plant produces heavy water, essential to the German nuclear weapons program.
-
01-03-1943: From March onwards, 5 special British support groups for the convoys are commissioned. Long range aircraft such as the B-24 Liberator, range 2,000 miles, are deployed to close the so called Atlantic gap. The new 10cm radar system (ASV III) enables efficient attacks on U-boat bases on the Gulf of Biscay.
-
01-03-1943: Admiral Dönitz deploys 50 U-boats at once (Wolf packs) against the enemy convoys in the Atlantic. They inflict serious losses.
-
01-03-1943: In March, the Arctic convoys are suspended due to the re-inforcement of the escort groups on the Atlantic convoy routes.
-
01-03-1943: In March, the first groups of Maquisards become active in Vercors and Savoie.
-
01-03-1943: In March the Norwegian Council of Churches protests against the labor deployment measures. A few leaders are arrested.
-
01-03-1943: In March, deportations from Prague, Vienna, Luxemburg and Macedonia to Treblinka.
-
01-03-1943: Soviet forces recapture Demjansk, Zaluchie and Lychkovo.
-
02-03-1943: The German forces begin withdrawing from Tunisia.
-
02-03-1943: Battle on the Sea of Bismarck. American and Australian aircraft and destroyers attack a Japanese convoy. The Japanese lose eight transports and four destroyers.
-
02-03-1943 - 02-03-1943: 19 transports from Westerbork to Sobibor in this period.
-
03-03-1943: The Soviets recapture Rzhev and Lgov.
-
05-03-1943: Concentration camp Riga-Kaiserwald is commissioned.
-
05-03-1943: Start of a four-month bombing offensive against the Ruhr valley. In the first attack, the Krupp works in Essen are bombed by 367 aircraft. 14 bombers do not return.
-
06-03-1943: Feldmarschall Rommel leads a German attack with tanks from Medenine on the British 8th Army on the Mareth line, without success though.
-
08-03-1943: Putera - center of people’s power for the war – is Installed on Java with Japanese approval. It is ruled by the Ampat Serangkai.
-
09-03-1943: General von Arnim is appointed supreme commander in North-Africa. Feldmarschall Rommel goes on sick leave.
-
10-03-1943: The guerilla leader on Sumatra, Lieutenant van Zanten, is arrested. See also March 25.
-
11-03-1943: Establishment of the Landstorm, a formation of volunteers who will see service in the Netherlands only.
-
12-03-1943: Vyasma is liberated by the Soviets.
-
12-03-1943: Half of the staff of the Jewish hospital in Berlin, along with their relatives, are deported to the death camps. The Jewish hospital would remain in operation for the rest of the war.
-
13-03-1943: Students in the Netherlands are to sign a declaration of loyalty before April 10.
-
13-03-1943: Failed assassination attempt on Hitler returning by plane from a visit at the eastern front. The time bomb, placed by an officer. does not explode due to the freezing temperature.
-
14-03-1943: The Krakow ghetto is liquidated.
-
15-03-1943: Deportations from Salonika and Thracia.
-
15-03-1943: Kharkov is captured again by the Germans after the city was liberated by the Soviets on February 16.
-
17-03-1943: Bulgaria offers resistance against the deportation of Jews.
-
19-03-1943: German troops recapture Bjelgorod. The onset of thaw brings the German advance to a halt.
-
20-03-1943: The British 8th Army launches an offensive against the Mareth line.
-
21-03-1943: Pastoral letter by Cardinal van Roey against the deportations.
-
21-03-1943: An attempt at assassination by Oberst Rudolph von Gersdorff on Hitler and other Nazi leaders fails. He cannot activate the bomb as Hitler leaves an exhibition too early.
-
22-03-1943: Hitler delivers a speech on Heroes Memorial Day: Die Steppen des Ostens haben noch einmal ihre Millionenmassen sich gegen Europa wälzen lassen" (The steppes in the east have had their millions waltz against Europe once more).
-
22-03-1943: Gas chamber/crematorium IV is opened in Auschwitz.
-
22-03-1943: The village of Khatyn (Belarus) is burned down by Schutzmannshaft battalion 118 and the population is massacred, 149 people, including 75 children, are killed.
-
24-03-1943: Physicians in the Netherlands go on strike in protest against the Ärztekammer (Chamber of Physicians).
-
25-03-1943: Lieutenant van Zanten (see March 10) is executed.
-
26-03-1943: Battle of the Komandorsky islands in the northern Pacific.
-
27-03-1943: A raid is carried out on the Central Population Registry in Amsterdam.
-
27-03-1943: U.S. troops attack the Fondouk pass in central Tunisia.
-
27-03-1943: British escort carrier HMS Dasher sinks in the Firth of Clyde after an internal explosion. This killed 379.
-
28-03-1943: Montgomery’s 8th Army breaches the Mareth line in Tunisia. Mareth, Toujane and Matmata are taken.
-
30-03-1943: The Höhere SS und Polizeiführer Hanns Rauter issues an order to the effect that as of April 10, Jews are no longer allowed to live in the provinces of Groningen, Friesland, Drenthe, Overijssel Gelderland, Zeeland, Noord-Brabant and Limburg. They are to go to camp Vught.
-
30-03-1943: An Allied bombardment of the Philips factory in Eindhoven claims 20 lives.
-
30-03-1943: The British 8th Army occupies Oudref; the British 1st Army recaptures Sejenane.
-
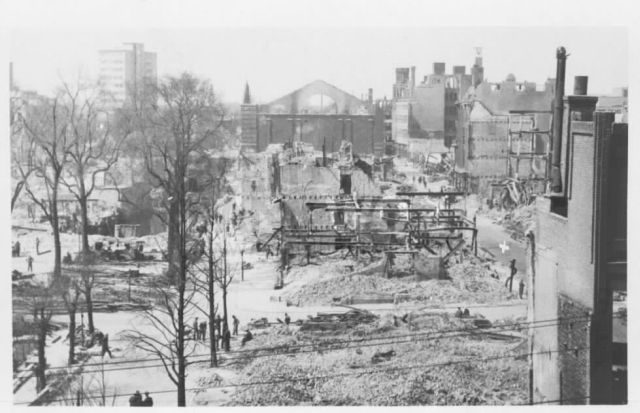
31-03-1943: Almost 100 bombers of the U.S.A.A.F. bomb Rotterdam, their target the Wilton-Feyenoord ship yard. The strong wind causes the bombs to miss the target resulting in some 400 dead and over 400 injured.
-
31-03-1943: Gas chamber/crematorium II is opened in Auschwitz.
-
01-04-1943: In April, Sweden is willing to negotiate with Germany about the release of 20,000 Jewish children. The United States and Great Britain refuse financial support.
-
01-04-1943: The mass gassings in Chelmno are abandoned.
-
01-04-1943: In April, General Vlassov establishes a Russian committee of liberation in Smolensk.
-
03-04-1943: Jan Dieters, one of the leaders of the C.P.N. is arrested.
-
04-04-1943: In Auschwitz, gas chamber/crematorium V is opened.
-
06-04-1943: Lou Jansen, one of the leaders of the C.P.N is arrested.
-
07-04-1943: Bolivia declares war on Germany and Italy.
-
07-04-1943: The British 8th Army and the U.S. 2nd Corps make contact in Tunisia.
-
07-04-1943 - 07-04-1943: Meeting between Hitler and Mussolini in Klessheim Castle near Salzburg, Austria.
-
08-04-1943: American troops break out into the region Maknassy. The U.S. 26th Brigade breaks through the Fondouk Pass.
-
09-04-1943: The prisoner-of-war camp Lublin is converted into a concentration camp.
-
12-04-1943: Hitler appoints Martin Bormann, head of the Party Chancellery, as his personal secretary.
-
14-04-1943: The British 8th Army reaches the Enfidaville line. French troops occupy Jebel Mansour.
-
16-04-1943: During an attack by the R.A.F. on the workshops of the Dutch railways in Haarlem, misdirected bombs hit adjacent residential areas. 85 people lose their lives.
-
18-04-1943: On an inspection tour over Bougainville, the aircraft carrying Japanese Admiral Yamamoto is shot down by an American P-38.
-
19-04-1943: Conference on Bermuda between delegates of the United States and Great Britain on the question of refugees.
-
19-04-1943: Three Belgian resistance fighters attack convoy XX on its way from Dossin barracks to an extermination camp. 17 Jews are liberated and another 232 later manage to escape from the train.
-
19-04-1943 - 19-04-1943: Jewish uprising in the Warsaw ghetto.
-
20-04-1943: In Great Britain Mr. Duncan Sandys is put in charge by the British government of an investigation into the threat of German long distance rockets.
-
21-04-1943: Enfidaville is occupied by the British.
-
22-04-1943: The first group of liaison officers land near Kibavksko Polje (Lika) in Yugoslavia.
-
26-04-1943: On occasion of a request by the Polish government in exile to the Red Cross to launch an investigation into the mass murder of Katyn, the Soviet Union severs her ties with the Sikorski government.
-
28-04-1943 - 28-04-1943: The last armored attack by the Axis powers results in the recapture of Djebel Bou Aoukaz.
-
29-04-1943: German general Christiansen calls on all former Dutch military personnel to report to be deported as prisoners-of-war.
-
29-04-1943: In Indonesia, the Keibodan (auxiliary police) and the Seinendan (system of youth organizations) are established officially.
-
29-04-1943: Start of the April-May strikes in Twenthe.
-
30-04-1943: The Aufenthaltslager für Juden (transit camp for Jews) is established in Bergen-Belsen.
-
30-04-1943: Spontaneous strikes erupt all over the Netherlands. The Dutch government in London calls on all not to cooperate in the deportation of Dutch former military personnel. The railway company decides not to join the strikes.
-
30-04-1943: The corpse of the fictitious Major William Martin washes up on the Spanish coast. This is a deception operation by the British secret service.
-
01-05-1943: In the Netherlands, Rauter proclaims martial law for the entire country. German patrols fire on groups of people. Strikers are arrested arbitrarily and many of them are transferred to camp Vught.
-
01-05-1943: The military administration on Sumatra (Dutch East Indies) which was led from Singapore is relocated to Fort De Kock.
-
01-05-1943: In May 1943, the balance in the battle in the Atlantic tips in favor of the Allies. 38 U-boats are sunk In the northern part of the Atlantic.
-
01-05-1943: In May, the Council of Resistance (R.V.V.) is established in Amersfoort by J. Thijssen. G. Wagenaar (C.P.N.) becomes top official.
-
01-05-1943: In May, Henry Frenay establishes the Service National Maquis (French underground organization).
-
01-05-1943: In May, the Forces Unies de la Jeunesse is established (Unified Youth movements).
-
01-05-1943: In May, the first meeting of the Counseil National de la Résistance (National Council for Resistance) is held, chaired by Jean Moulin.
-
01-05-1943: In May, Unternehmen Schwarz (Operation Black) gets under way; actions by German troops against Tito’s partisans.
-
01-05-1943: Stalin’s order of the day: Only Germany’s unconditional surrender will lead to peace in Europe.
-
01-05-1943 - 01-05-1943: The OD warns the secret service in London by telegram that the Dutch SOE network has been infiltrated by the Germans.
-
01-05-1943 - 01-05-1943: Between May and June, the third Sauckel Aktion is launched in France.
-
02-05-1943: A total of 27 Dutchmen are executed for violation of martial law.
-
03-05-1943: The strikes in the Netherlands have all but ended.
-
04-05-1943: Quiet seems to have returned to the Netherlands, again a number of death sentences is carried out.
-
05-05-1943: The British recapture Djebel Bou Aoukaz.
-
05-05-1943 - 05-05-1943: A group of Jews go into hiding in a cave near Korolivka, Ukraine to escape German persecution. Some of them will spend up to 344 days underground before the area is liberated by the Red Army in April 1944.
-
06-05-1943: All Dutch males between the ages 18 and 35 are obliged to report to a labor office.
-
07-05-1943: In the early morning, British troops enter Tunis. American and French troops capture the naval base at Bizerta.
-
08-05-1943: In Belgium, General von Falkenhausen blames the secretaries-general for their lack of cooperation. Out of all the Belgians called up for work in Germany, 60% has gone into hiding.
-
09-05-1943: In Burma, British and Indian troops evacuate the Boethedaoeng base on the river Majoe on the Bengal border.
-
09-05-1943: Spanish head of state Franco calls for peace as the war has reached a phase in which none of the belligerents can destroy its opponent.
-
11-05-1943: American troops go ashore on the island of Attu in the Aleuthians in the Pacific.
-
12-05-1943: At the Trident Conference in Washington, the Combined Chiefs of Staff tentatively set the date for Operation Overlord at May 1, 1944.
-
12-05-1943: In the Netherlands, the class of 1921 is to report to the labor offices.
-
12-05-1943: Uruguay and Vichy-France sever their diplomatic ties.
-
13-05-1943: The Germans accept the Allied demand of unconditional surrender of the troops near Cape Bon in Tunisia. 250,000 German and Italian soldiers surrender, including German general Jürgen von Arnim and the Italian general Messe.
-
13-05-1943: In Dutch newspapers, the announcement is made that all radios will be confiscated. They are to be handed in to police stations or post offices.
-
13-05-1943: The last German and Italian troops in North-Africa surrender.
-
14-05-1943: Allied bombers attack the German port of Kiel.
-
14-05-1943: The Allies impose a blockade on the island of Pantelleria in the Strait of Sicily.
-
14-05-1943: Jews of mixed marriages in Westerbork face the choice: sterilization or deportation.
-
14-05-1943: In the past 10 days, the Nazis have liquidated 70,000 Jews in the Warsaw ghetto. Out of the 56,000 who have surrendered, 7,000 have been shot on the spot, the remaining have been deported to concentration camps.
-
14-05-1943: A Japanese submarine sinks the Australian hospital ship H.M.A.S. Centaur; 299 people lose their lives.
-
15-05-1943: In the Netherlands, the Federation of Broadcasting stations is established illegally. J.B. Broeksz (VARA) is appointed chairman, W. Vogt (AVRO) is appointed secretary.
-
16-05-1943: The Möhne and Eder dams in the Ruhr valley are bombed by R.A.F. 617 Squadron, with Lancasters specially converted to carry the bouncing bomb. The dams provide electricity and water for the Ruhr area. Also kn0wn as the Dam Buster Raid.
-
16-05-1943: The uprising in the Warsaw ghetto is over. Some 14,000 Jews have been killed, 22,000 deported to extermination camps and 20,000 to labor camps.
-
19-05-1943: Berlin is officially declared Judenfrei (free of Jews).
-
22-05-1943: Admiral Karl Dönitz, commander of the Kriegsmarine, suspends U-boat operations in the north Atlantic due to the severe losses in ships and U-boats.
-
22-05-1943: 30,000 copies of the first issue of the pamphlet De Vliegende Hollander (Flying Dutchman) are dropped over the Netherlands.
-
22-05-1943: Radio Moscow announces the decision of May 15, 1942 to dissolve the Komintern.
-
22-05-1943: Dropping of SOE agents Oscar de Brey, Anton Mink and Laurentius Punt. They are the last of about 50 officers to be arrested as part of the England Spiel.
-
23-05-1943: The R.A.F. unleashes a massive bombardment on Dortmund.
-
25-05-1943: End of the Trident conference in Washington. The plan of operation against Japan is approved by the American and British chiefs of staff.
-
26-05-1943: An Axis army, 120,000 strong launches an attack on 16,000 Communist partisans in Monte Negro, Yugoslavia.
-
29-05-1943: A heavy bombardment on Wuppertal by the R.A.F. claims 2,450 dead.
-
30-05-1943: Josef Mengele is appointed camp doctor in Auschwitz.
-
31-05-1943: Japanese conference on the future status of Indonesia.
-
01-06-1943: The United States start unlimited submarine warfare against Japanese shipping.
-
02-06-1943: British destroyer H.M.S. Jervis and the Greek vessel Vasiilisa Olga attack an Italian convoy, the Italian destroyer Castore and two transports are lost.
-
03-06-1943: Rivaling French leaders Charles de Gaulle and Henri Giraud decide to jointly lead the Comité National de la Résistance (National; committee of resistance) in France.
-
03-06-1943: Attempt at murder on F.E. Posthuma, member of Mussert’s State Secretariat.
-
03-06-1943: Establishment of the Comité Français de Libération National (French Committee of National Liberation) in Algiers.
-
03-06-1943: Unternehmen Cottbus. The Germans launch an offensive against partisans in the Borisov area.
-
03-06-1943: Admiral Halsey orders the start of Operation Toe Nails. The object is to capture Munda on New Georgia and use it as spring board for the island hopping campaign.
-
04-06-1943: General Giraud is named supreme commander of the Free French Forces.
-
10-06-1943: Start of Operation Point Blank. The offensive by British and American bombers to crush the morale of the German people and the economy.
-
10-06-1943: Jean Moulin is arrested in the vicinity of Lyon.
-
11-06-1943: The British invade Pantelleria.
-
11-06-1943: Himmler orders the liquidation of all Jewish ghettos in Poland.
-
12-06-1943: British King George arrives in Tripoli in order to visit the Allied troops.
-
12-06-1943: The Italian island of Lampedusa surrenders to the British.
-
13-06-1943: In the Netherlands, distribution of replacement materials is started.
-
20-06-1943: The Italian government orders the evacuation of Naples and other Sicilian cities.
-
23-06-1943: British aerial photographs of Peenemünde reveal " 40 feet long objects with fins," lying horizontally on vehicles surrounded by an earthen wall.
-
25-06-1943: In Auschwitz, crematorium III is ready for operation.
-
26-06-1943: General-kommissar Fritz Schmidt has died.
-
28-06-1943: Hitler orders the highest priority for the construction of special re-inforced launch sites for the V-1 along the Strait of Calais.
-
30-06-1943: Churchill delivers a speech defending the Allied demand for unconditional surrender.
-
30-06-1943: Operation Cartwheel. Landings on New Georgia in the Solomon islands, on Woodlark and Kiriwana in the Tobriand islands and in Nassau Bay on New Guinea.
-
01-07-1943: After having witnessed a test launch of a V-1, Hitler orders the highest priority for its further development.
-
03-07-1943: The Greek King promises free elections within six months after the liberation.
-
04-07-1943: At 23:05, General Vladyslav Sikorski loses his life in a plane crash. Stanislav Mikolaiczyk succeeds him as Prime Minister.
-
05-07-1943: Unternehmen Zitadelle or the battle of Kursk. The German launch the largest tank battle in history. The Soviets are aware of their plans and launch a heavy pre-emptive attack on the massed German forces just prior to their attack.
-
06-07-1943: Battle in the Gulf of Kula. The Japanese only manage to put 850 men ashore on New Georgia and have to turn back. Japan loses three destroyers, the U.S. loses one cruiser.
-
07-07-1943: The Japanese stronghold on Mumbo, 10 miles inland from Salamaua on Papua New Guinea is attacked by Australian troops.
-
08-07-1943: Jean Moulin dies after having been brutally tortured by the Gestapo.
-
09-07-1943: The invasion of Sicily – Operation Husky – starts with chaotic landings by American and British paratroops.
-
10-07-1943: An invasion armada of 2,500 vessels takes Montgomery’s 8th Army and Patton’s 7th Army to the south of Sicily. The Italians are utterly surprised as they do not expect an invasion in stormy weather.
-
11-07-1943: The Hermann Göring Panzerdivision almost makes contact with the Americans on the coast near Gela and Licata but paratroopers prevent a counter attack.
-
12-07-1943: Battle of Kolombangara – second battle of Kula; the Japanese manage to put 1,200 men ashore near Vila. One Japanese cruiser is lost, the U.S.A. lose a destroyer and three cruisers are damaged.
-
12-07-1943 - 12-07-1943: In Krasnagorsk, German refugees and prisoners-of-war establish the Nationalkomittee Freies Deutschland. (National committee of free Germany).
-
13-07-1943: Hitler puts a stop to Operation Zitadelle. What a grand victory should have become for the Germans has turned into catastrophe.
-
15-07-1943: The American 7th Army drives westwards towards the capital Palermo which will be captured in an armored assault.
-
15-07-1943: Soviet troops launch numerous heavy counter attacks against the retreating Germans.
-
16-07-1943: Roosevelt and Churchill appeal to the Italian population to surrender.
-
16-07-1943: The American 7th Army enters Comino in Italy.
-
17-07-1943: In the northern part of Amsterdam, residential areas are hit by stray bombs during a raid by the U.S.A.A.F. on the Fokker works.
-
17-07-1943: The appeal by Roosevelt and Churchill (see 07-16) is dropped over Rome by Allied aircraft in the form of a pamphlet.
-
19-07-1943: The American 7th Army manages to enter the ports of Trapani and Marsala on the west coast of Italy.
-
19-07-1943: Meeting between Hitler and Mussolini in Feltre.
-
20-07-1943: The British carry out the first staged bombing attacks. They bomb Friedrichshafen first, then fly on to North-Africa to refuel and on their return flight to Great Britain attack the Italian naval base La Spezia.
-
20-07-1943: The Joint Chiefs of Staff order Admiral Nimitz to draft plans for the capture of the Gilbert islands.
-
22-07-1943: The German High Command orders the troops around Orel to withdraw to prepared lines east of Briansk.
-
22-07-1943: Units of the American 7th Army occupy Palermo.
-
23-07-1943: The Germans have been pushed back to the start positions of Unternehmen Zitadelle.
-
24-07-1943: Grandi, chairman of the Great Fascist Council, submits a motion to Mussolini suggesting to transfer personal charge of the war to the King.
-
24-07-1943 - 24-07-1943: Operation Gomorrah; R.A.F. Bomber Command and the U.S. 8th Air Force launch various saturation attacks on Hamburg. The attacks claim some 30,000 dead, some 50,000 injured and 800,000 people become homeless. In these operations, Windows is used for the first time, strips of aluminum foil jamming German radar.
-
25-07-1943: The King of Italy fires Mussolini and has him arrested. Marshal Pietro Badoglio forms a new government that will last only six weeks.
-
25-07-1943: Operation Achse is launched: German troops enter Italy.
-
27-07-1943: An Allied bombardment on Hamburg triggers a giant firestorm.
-
28-07-1943: In Italy, the Fascist Party and the Great Fascist Council are dissolved.
-
28-07-1943: The Japanese complete a successful evacuation – unnoticed by the Americans – of the island of Kiska in the Aleuthians.
-
31-07-1943: At the end of July, the German police rolls up the illegal group Het Zwaantje (little swan) led by the Delfzijl physician A. Oosterhuis. The group maintained contact with Great Britain via the Swedish route.
-
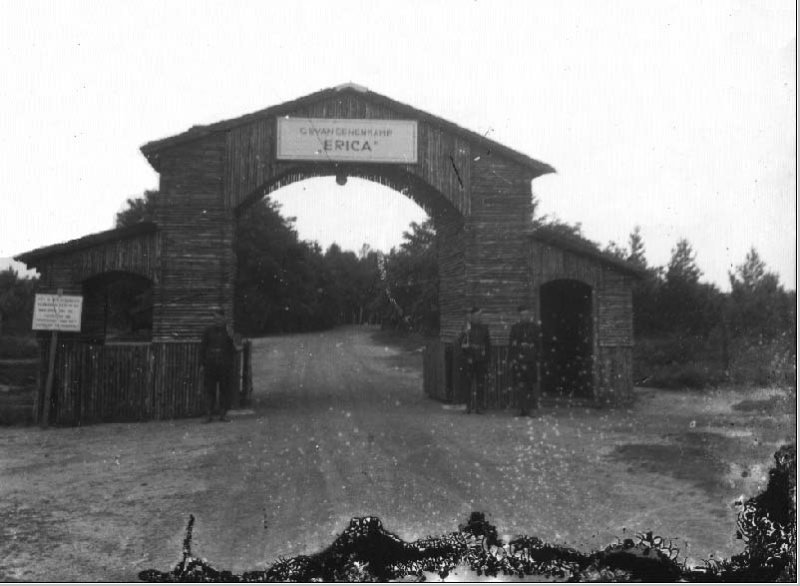
31-07-1943: Mid 1943, the penal camp Erika near Ommen is opened.
-
01-08-1943: 178 American bombers fly 932 miles from Libya in order to bomb the oil fields of Ploesti in Romania. These fields are of vital importance to the Axis powers.
-
01-08-1943: Allied offensive against enemy lines in northeastern Sicily.
-
01-08-1943: Japan designates Birma as an independent nation. Head of State is U Ba Maw. Birma declares war on Great Britain and the United States.
-
01-08-1943: In August, the administration of the Mouvements Unis de la Résistance (United resistance movements) takes up residence in Paris.
-
01-08-1943: In August, the fourth Sauckel Aktion is carried out in France.
-
02-08-1943: Hitler orders Feldmarschall Erich von Manstein to hold on around Kharkov.
-
02-08-1943: An uprising in extermination camp Treblinka results in the destruction of the crematoria.
-
03-08-1943: The Italian regime sounds out the Allies about peace.
-
03-08-1943: The Italians abandon Sicily. The British capture Catania on the fifth.
-
05-08-1943: The Red Army recaptures Orel and Belgorod. The Voronezh and Steppe fronts are now close to Kharkov.
-
05-08-1943: The Americans capture the important air field of Munda on New Georgia. Japanese resistance collapses.
-
05-08-1943: In the Plötzensee prison in Berlin, sixteen members of the German resistance (13 women and 3 men) are executed, one of them is Cato Bontjes van Beek.
-
06-08-1943: In Italy, German reinforcements are arriving.
-
06-08-1943: Four Japanese destroyers carrying troops and supplies for Kolombagara on New Georgia run into six American destroyers in the Gulf of Vela at night and are destroyed.
-
08-08-1943: In the Netherlands, fruit and vegetables are put on ration.
-
13-08-1943: Churchill and Roosevelt meet in Quebec for the first time.
-
13-08-1943: The Soviets launch a new offensive near Spas-Demensk, east of Smolensk and recapture the town.
-
15-08-1943: After Americans and Canadians have landed on Kiska, they find out the 4,500 Japanese have already left.
-
15-08-1943: The Aleuthians are back in American hands.
-
16-08-1943: The Bialystok ghetto no longer exists.
-
17-08-1943: American troops reach Messina, Sicily.
-
17-08-1943 - 17-08-1943: R.A.F. Bomber Command launches a heavy bombing attack with 597 bombers on Peenemünde. The Germans abandon Peenemünde. Assembly is relocated to Niedersachswerfen in the Harz. Henceforth, test launches are conducted in Blitzna in Poland.
-
23-08-1943: Fourth battle for Kharkov; the city is recaptured by the Soviets and will never fall in German hands again.
-
25-08-1943: The appointment of Lord Louis Mountbatten to Supreme Allied Commander in southeast Asia is announced.
-
25-08-1943: After U.S. troops have recaptured the port of Bairoko on New Georgia, the hostilities on this island are decided in favor of the Americans.
-
28-08-1943: The Danish government steps down after ignoring the German order to punish saboteurs.
-
28-08-1943: The Soviets launch offensives against Taganrog, Smolensk and in the direction of Gluchov and Rylsk.
-
30-08-1943: Taganrog on the Sea of Azov is recaptured by the Soviets.
-
30-08-1943: SOE agents Pieter Dourlein and Ben Ubbink, arrested within the framework of the Englandspiel, escape from Kamp Haaren.
-
01-09-1943: In September, concentration camp Klooga in Estonia is opened.
-
01-09-1943: In September the Gestapo rolls up the Berlin group Die Europäische Union (European Union) which wanted to keep in touch with foreign forced laborers.
-
03-09-1943: Montgomery’s 8th Army establishes a bridgehead in Calabria from Sicily. It happens without resistance as the Germans in southern Italy have been ordered to withdraw.
-
03-09-1943: Italy signs the armistice in Syracuse on Sicily.
-
04-09-1943: Stalin meets the three most important metropolises of the Russian Orthodox church. He allows them to select a patriarch again.
-
04-09-1943: Allied troops recapture Lae and Salamauain on New Guinea.
-
06-09-1943: In Belgium, the years 1920 and 1921 are called up for mandatory employment in Germany.
-
07-09-1943: Instruction by Rauter as to the introduction of the second distribution card.
-
08-09-1943: The Allies make the official announcement: Italy has surrendered. The Germans occupy the north and set up coastal fortifications in case of Allied landings.
-
08-09-1943: With Unternehemn Fall Achse, Hitler commands the disarmament of the Italian army.
-
08-09-1943: The British 8th Army comes ashore near Pizzo on the Gulf of Eufemia.
-
08-09-1943: Stalino and Krasnoarmeskojo are liberated by the Soviets. The entire Donetz basin is now liberated.
-
09-09-1943: The American 5th Army commanded by General Mark Clark and the British 10th Corps land in the Gulf of Salerno.
-
10-09-1943: The Germans withdraw 25,000 men via Corsica from Sardinia to Italy. Early October, 7,000 French and American troops land on Corsica.
-
10-09-1943: In northern Italy, Italian troops surrender to the Germans. The British 8th Army occupies Tarente. Under Kesselring’s command, German air borne troops occupy Rome after heavy fighting.
-
11-09-1943: Salamaua on New Guinea is recaptured by American and Australian troops.
-
11-09-1943: Allied landings at Tarente.
-
12-09-1943: SS troops commanded by Lieutenant-colonel Otto Skorzeny rescue Mussolini from his imprisonment on the Gran Sasso in the Abruzzen mountains.
-
12-09-1943: German troops launch a fierce counter attack around Salerno and threaten the bridgehead. The Allies are saved by counter attacks and heavy artillery barrages.
-
12-09-1943: The underground parties in Italy form a Committee of National Liberation. They demand the abdication of the King. Beginning of a period of resistenza.
-
13-09-1943: Heavy German attacks near Salerno are repulsed by landing of paratroops commanded by Major-general Ridgeway.
-
14-09-1943: Hitler and Mussolini meet in Rastenburg.
-
15-09-1943: Special British forces come ashore on Kos. The island is the spring board for the offensive against the German stronghold on Rhodos.
-
15-09-1943: Establishment of concentration camp Kauen in Lithuania; concentration camp Vaivara is opened in Estonia.
-
15-09-1943: Mussolini proclaims the puppet state Republic of Salo.
-
16-09-1943: Lae falls in Allied hands.
-
16-09-1943: The British 8th Army occupies Sapri. The U.S. 5th Army launches an offensive near Salerno. British and American troops meet.
-
16-09-1943: Novorossiisk on the Black Sea is liberated by the Soviets.
-
17-09-1943: The Soviets take Briansk and Besjhiza.
-
18-09-1943: Successful progress of the attacks by Soviet forces in the direction of Kiev, Saporosje, Melitopol, Dnjepropetrowsk, Poltava, Krasnograd, Smolensk, Roslavi and near Novorossiisk.
-
18-09-1943 - 18-09-1943: Start of the special mission, code named Macmis, of the British officer Fitzroy MacLean to Tito’s partisans. He is dropped over western Bosnia.
-
21-09-1943: Australian commandoes enter Singapore harbor in canoes and sink two Japanese transports.
-
21-09-1943: The Americans capture the island of Arundel in the Solomon islands.
-
22-09-1943: The Soviet 13th Army crosses the Dnepr south of Kiev, establishing bridgeheads as they go.
-
22-09-1943: The Japanese on the Huon peninsula are besieged by Allied landings and naval bombardments.
-
22-09-1943: British midget submarines attack a naval unit in the Altenfjord in Norway and cripple the Tirpitz.
-
22-09-1943: The 78th Division of 8th Army lands in Bari. The British move up and in five days, Foggia and its valuable air field are captured.
-
23-09-1943: Mussolini announces the formation of the Italian Social Republic in northwestern Italy. This republic transfers authority over certain areas to Germany however.
-
24-09-1943: The Germans executed 136 Italian officers of the Acqui division on the Greek island of Kefalonia. In the following days, more than 5,000 soldiers of the division were also shot.
-
25-09-1943: During the continuing Soviet offensive Smolensk is recaptured. Heeresgruppe Mitte retreats in disarray.
-
26-09-1943: Soviet troops reach the Dnepr in various places.
-
26-09-1943 - 26-09-1943: The Danish resistance sets up an escape route. Some 7,500 Jews manage to escape.
-
29-09-1943: The first Silbertanne murder in Meppel, the Netherlands.
-
30-09-1943: In Fallersleben mass production of the V-2 starts at the end of the month.
-
01-10-1943: The British enter Naples and the American 5th Army captures the main port.
-
01-10-1943: In October, the Germans issue measures against the Jews in Denmark. Over 6,000 out of the 8,000 Danish Jews manage to go into hiding or escape to Sweden.
-
01-10-1943: Averell Harriman is appointed U.S. Ambassador in Moscow.
-
01-10-1943 - 01-10-1943: Period of struggle between the E.L.A.S. and the E.D.E.S.; the Greek Communist resistance movement unleashes a civil war in order to enable transfer of power after the liberation.
-
02-10-1943: The Japanese have abandoned the island of Kolombangara in the Solomons.
-
03-10-1943: Kos is captured by 12,000 German paratroops. Some 900 Allied and 3,000 Italian soldiers are taken prisoner-of-war. The Germans execute 90 Italian officers for collaboration with the enemy.
-
03-10-1943: On the island of Java, the Volunteer Army P.E.T.A. (army for the defense of the fatherland) is established under Japanese command. Most of the men come from the Seinendan (See April 29).
-
04-10-1943: In Poznan Himmler talks openly about the Endlösung (Final solution).
-
06-10-1943: Two British cruisers and destroyers attack a German convoy bound for Leros. Seven enemy transports and an escort vessel are sunk.
-
06-10-1943: Battle of Vella Lavella in the Solomons.
-
07-10-1943: Start of the Soviet autumn offensives on a broad front from Witebesk up to the Taman peninsula.
-
07-10-1943: The entire Taman peninsula is liberated by the Soviets.
-
07-10-1943: On Wake island, some 100 American prisoners-of-war are executed by Japanese soldiers.
-
09-10-1943: The Red Army reaches the Kerch Strait. With this, the entire northern Caucasus is recaptured.
-
10-10-1943: Strong Soviet units are transferred to the bridgeheads on the Dnepr and destroy strong German positions around Zaporizzya and Melitopol.
-
10-10-1943: Owing to misidentification of a target of opportunity, the city of Enschede is severely damaged in an attack by the U.S.A.A.F. Some 150 civilians lose their lives.
-
12-10-1943: Heavy American bombings on Rabaul, New Britain.
-
12-10-1943: In accordance with the Anglo-Portuguese treaty of 1373, the Portuguese government has offered facilities on the Azores to England for her shipping, this to protect the merchant navy.
-
12-10-1943 - 12-10-1943: The Polish Armed Forces in the East experience their baptism of fire during an offensive on Lenino. Thousands of Poles are killed or missing.
-
13-10-1943: The government of Marshal Pietro Badoglio in southern Italy declares war on Germany.
-
13-10-1943: The American 5th Army commanded by General Mark Clark crosses the river Volturno in Italy.
-
13-10-1943: The council of Ministers of Mussolini’s republic establishes special courts to sentence the "traitors of July 25 1943".
-
14-10-1943: Declaration of independence of the Philippines under President José Laurel.
-
14-10-1943: Uprising of inmates in camp Sobibor. Shortly after, the mass gassings are suspended.
-
16-10-1943: In Rome, Jews are rounded up. Some 7,000 out of the 8,000 manage to go into hiding.
-
17-10-1943: The Soviets break out of the bridgehead at Krementsjug on the right bank of the Dnepr; they cross the river south of Gomel.
-
18-10-1943: Heavy American bombardments on Bougainville in the Solomons.
-
18-10-1943 - 18-10-1943: Third Moscow conference between the secretaries of Foreign Affairs Molotov, Eden and Cordell Hull. Stalin declares himself willing to meet Roosevelt and Churchill shortly.
-
23-10-1943: The first train load of Jews from Rome arrives in Birkenau.
-
23-10-1943: Melitopol is liberated.
-
24-10-1943: In Indonesia, the M.I.A.I. (Madjelis Islam A'la Indonesia) a federation of religious Islamic associations is dissolved. It was founded in 1937 and re-established on July 13, 1942.
-
25-10-1943: Allied prisoners-of-war and local forced laborers complete the Birma railroad.
-
25-10-1943: Dnjepropetrovsk is liberated.
-
25-10-1943: Memo by General von Rundstedt: in his opinion, the defense of the French coast is insufficiently guaranteed. He wants a different strategy in order to launch quick and effective counter attacks in case of an eventual landing.
-
27-10-1943: Ir. Louwes, Secretary-general of Food Distribution warns the Hauptabteilung Ernährung und Landwirtschaft (head office of food and agriculture) about the poor conditions of feeding and health of the Dutch population. He asks far reaching changes in export and the deliveries to the Wehrmacht.
-
30-10-1943: Soviet forces reach the northern Crimea and have chased the Germans from the left bank of the Dnepr.
-
31-10-1943: Soviet units have reached Perekop.
-
31-10-1943: At the end of October, the RAF flights over the Netherlands are suspended for the dropping of weapons and equipment because of the high losses (caused by the Englandspiel).
-
01-11-1943: The Americans land on Bougainville, the last objective in the Solomons.
-
01-11-1943 - 01-11-1943: Concentration of Soviet troops near Oranienbaum (delivered by the Baltic Fleet) in preparation of the final offensive on the Leningrad front.
-
03-11-1943: British aerial reconnaissance photographs launch sites, the so called ski ramps in northern France after having been tipped off about these sites by a French underground source. In the last week of October, 95 of such sites have been discovered.
-
03-11-1943: Führerweisung 51: In connection with the defense of the European west coast, Hitler orders heavier arms for the troops in the west.
-
06-11-1943: The Soviets recapture Kiev. 17th Army is trapped in the Crimea as a result of Hitler’s Haltebefehl.
-
06-11-1943: Stalin’s speech to the Supreme Soviet: "The cause of German Fascism is lost."
-
06-11-1943: Soviet units land on the Kerch peninsula.
-
09-11-1943: General de Gaulle alone is president of the Comité de la Libération Nationale (Committee of National Liberation).
-
10-11-1943: The Germans have captured the islands of Kos and Leros.
-
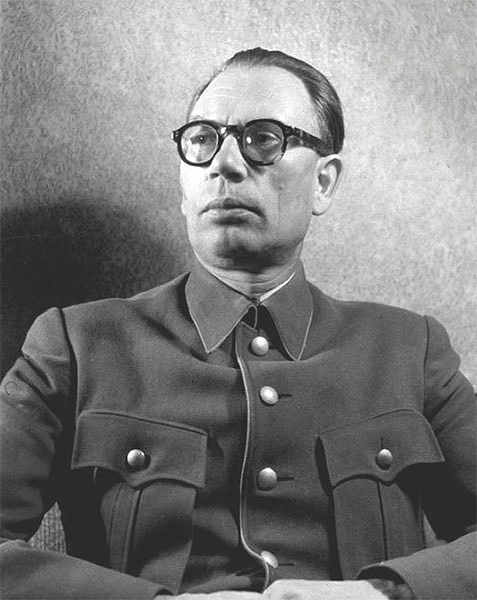
11-11-1943: Auschwitz commander Rudolph Höss is promoted to chief inspector of concentration camps. He is succeeded by Liebehenschel as camp commander.
-
13-11-1943: On an aerial photograph of Peenemünde of June 23, British officer Babington Smith of the Central Interpretation Unit discovers an unidentified mini aircraft (V-1).
-
13-11-1943: Establishment of the Landwacht; a protective unit of the N.S.B. against attacks by the resistance.
-
13-11-1943: Almost all textile products in the Netherlands are only available with a special permit.
-
15-11-1943: Great Britain resumes the convoys to Russia.
-
15-11-1943: The Japanese transport Kinugawa Maru is beached on Guadalcanal.
-
16-11-1943: Germany captures the island of Leros and so thwarts a British attempt to capture the Dodekanesos.
-
18-11-1943: Great Britain starts a five-month bombing offensive against Berlin. Over 6,100 people are killed, 18,400 injured and large parts of the city are turned to rubble.
-
20-11-1943: The Allies resume their offensive against Rome but are stopped short at the Gustav line.
-
20-11-1943: The SOE agents Ubbink and Dourlein who have escaped from Kamp Haaren send an extensive telegram from Bern to London. They mention here the German infiltration of the SOE network. London now suspects danger in the Netherlands.
-
22-11-1943: Churchill, Roosevelt and Chang Kai Chek meet in Cairo. The main subject of discussion is post-war China and Birma.
-
23-11-1943: The last Japanese resistance on Makin and Tarawa is eliminated.
-
23-11-1943: Three agents arrested in the context of the England Spiel (A. van der Giessen, J. van Rietschoten and A. Wegner) escape from Kamp Haaren. All three are later arrested.
-
24-11-1943: The Japanese submarine I 175 sinks the American escort carrier U.S.S. Liscombe Bay off Makin. 644 sailors lose their lives.
-
26-11-1943: Gomel is liberated.
-
28-11-1943: Churchill, Roosevelt and Stalin meet in Teheran (Iran) and discuss, among other subjects, Overlord, the invasion of Normandy. The Soviets have been demanding for some time to open a second front.
-
01-12-1943: Air Marshal R.M. Hill, in charge of Britain’s air defense, orders to draft a plan to defend Great Britain against flying bombs and rockets.
-
02-12-1943: The first trainload of Viennese Jews arrives in Birkenau.
-
05-12-1943: The U.S. 8th Air Force launches Operation Crossbow: bombing the "ski ramps" in Northern France.
-
06-12-1943: Fourth visit of Mussert to Hitler.
-
09-12-1943: Marshal Badoglio, Italy’s new Prime Minister announces that Italian units have joined the Allies.
-
12-12-1943: Feldmarschall Rommel is ordered by O.K.W. to inspect the coastal defenses of the Atlantikwall. As supreme commander of Heeresgruppe B, he is subordinate to the ObWest, Gerd von Rundstedt.
-
15-12-1943: American troops land on the Arawe peninsula on New Britain in the Solomons.
-
15-12-1943 - 15-12-1943: Three Germans and a collaborator from Kazachstan are indicted for war crimes by a Soviet tribunal in Kharkov. They are sentenced to death and publicly hanged on December 19.
-
20-12-1943: Despite continuing Japanese resistance, the Allies have all but captured the Huon peninsula.
-
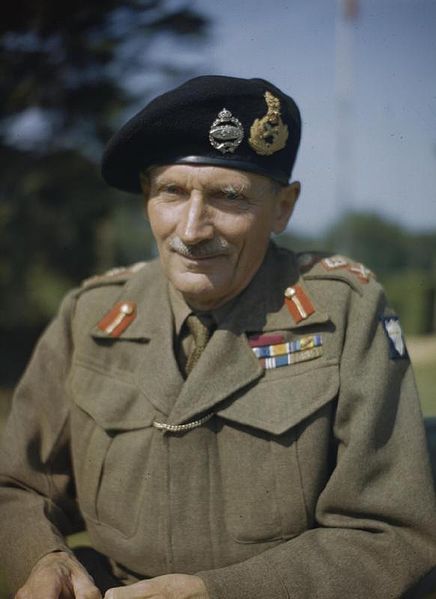
24-12-1943: President Roosevelt and Churchill announce the appointment of General Eisenhower to supreme commander of the Allied invasion force for Operation Overlord. General Sir Bernhard L. Montgomery is named supreme commander of the British forces for Overlord. He will be supreme commander of all land forces for Overlord until Eisenhower has established his headquarters in France.
-
24-12-1943: Sir Henry Maitland Wilson is appointed supreme commander of the Allied forces in the Mediterranean.
-
26-12-1943: The German battleship Scharnhorst is sunk off the North Cape. Out of her crew of 1,800 only 36 survive the tragedy.
-
31-12-1943: At the close of 1943, Feldmarschall von Rundstedt orders the construction of a second line of defense a few miles behind the existing coastal defenses.
-
31-12-1943: Zhitomir is recaptured by the Soviets.
-
31-12-1943: Massive Allied attack on New Britain. The 1st Marines Division enters Cape Gloucester.
-
31-12-1943: The 8th Air Force attacks attacks a repair shop for aero engines near Paris.